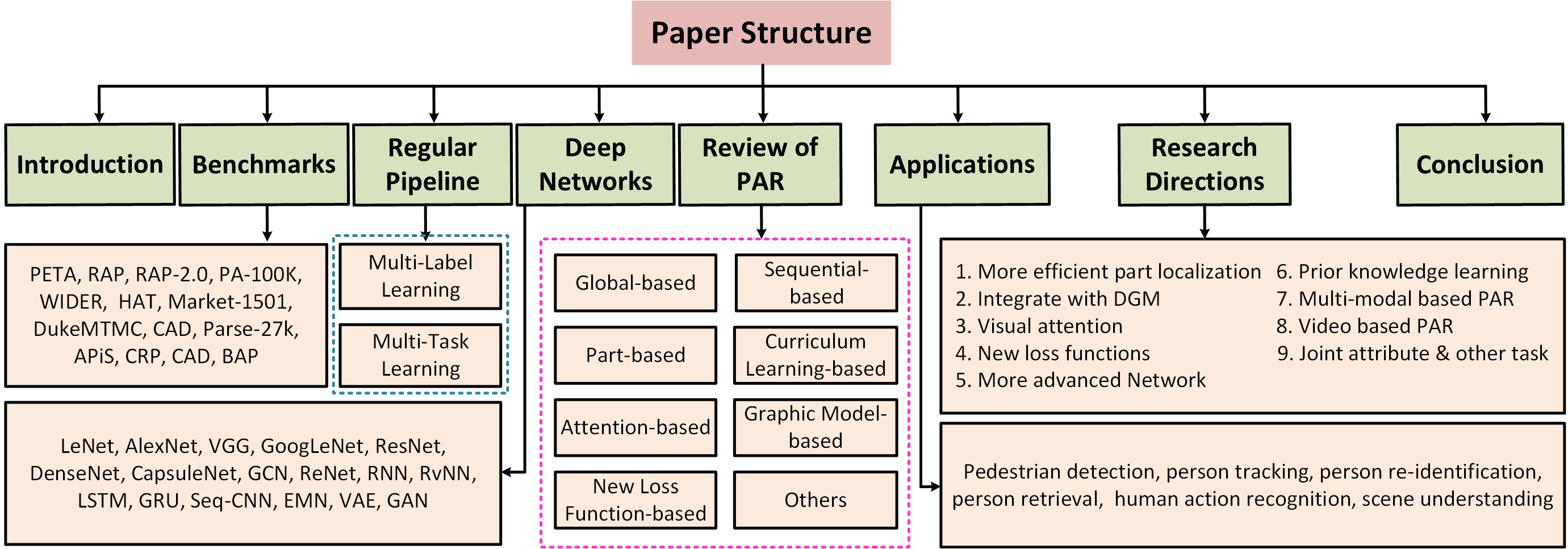
梳理 Pedestrian Attribute Recognition(行人属性识别) 相关介绍,数据集,算法
Intro
Foreword
- (reference https://arxiv.org/pdf/1901.07474.pdf https://github.com/wangxiao5791509/Pedestrian-Attribute-Recognition-Paper-List)
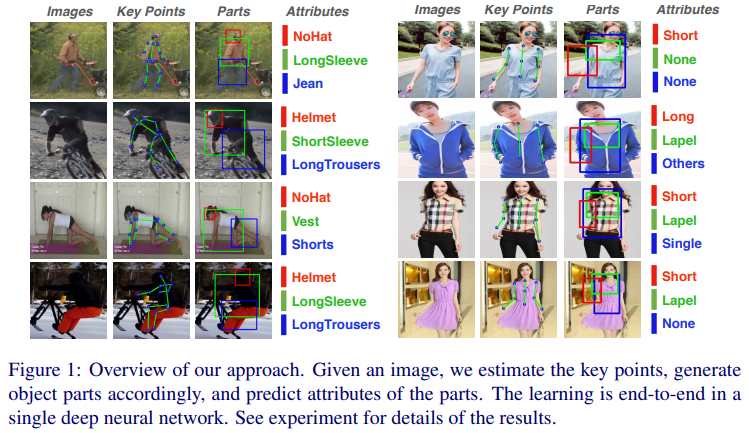
What is Pedestrian Attribute Recognition
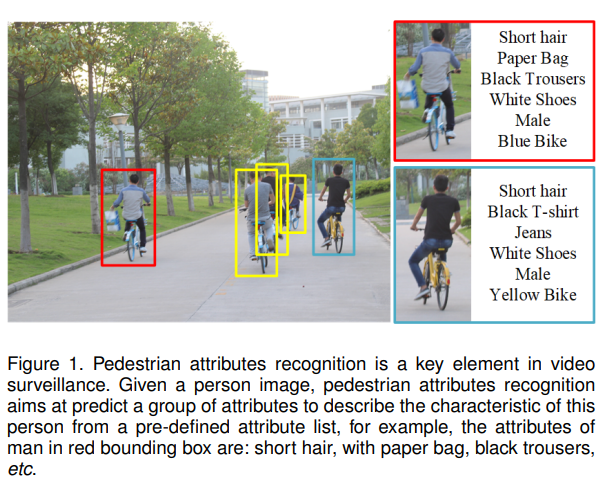
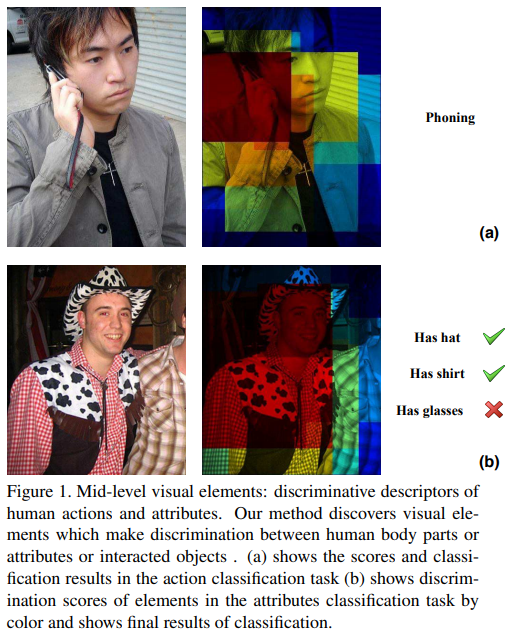
- Pedestrian attributes, are humanly searchable semantic descriptions and can be used as soft-biometrics in visual surveillance, with applications in person re-identification, face verification, and human identification. Pedestrian attributes recognition (PAR) aims at mining the attributes of target people when given person image, as shown in follow.
- 行人属性是人为的可搜索的拥有语义信息的描述,可以用来作为一种软生物识别技术在视频监控领域,在re-id,人脸识别,人体识别上都有应用。下面是行人属性识别的展示
Traditional practice and more
- Traditional pedestrian attributes recognition methods usually focus on developing robust feature representation from the perspectives of hand-crafted features, powerful classifiers or attributes relations. Some milestones including HOG [1], SIFT [2], SVM [3] or CRF model [4]. However, the reports on large-scale benchmark evaluations suggest that the performance of these traditional algorithms is far from the requirement of realistic applications. Over the past several years, deep learning have achieved an impressive performance due to their success on automatic feature extraction using multi-layer nonlinear transformation, especially in computer vision, speech recognition and natural language processing. Several deep learning based attribute recognition algorithms has been proposed based on these breakthroughs.
- 传统的做法基本就是 手工设计的特征 + 强力的分类器/属性关联 ,如 HOG SIFT SVM CRF,但是这些在大规模的benchmark上就没那么好使了。在过去的这些年里,深度学习方法因其自动强大的特征提取器带来了令人印象深刻的表现,在行人属性识别上也是如此。
PROBLEM FORMULATION AND CHALLENGES
- Multi-views 对同一对象,不同视角观察带来的差异
- Occlusion 遮挡
- Unbalanced Data Distribution 不平衡的 数据|lable 分布
- Low Resolution 低分辨率
- Illumination 亮暗在一日内变化大
- Blur 模糊
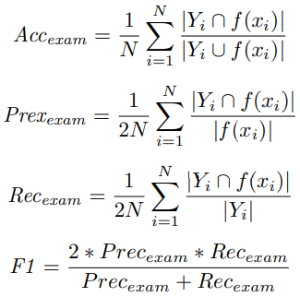
Evaluation Criteria
REGULAR PIPELINE FOR PAR
- Multi-task Learning
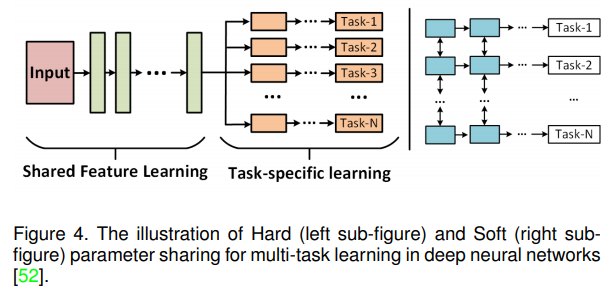
- deep learning based multi-task learning, i.e. the hard and soft parameter sharing. The hard parameter sharing usually take the shallow layers as shared layers to learn the common feature representations of multiple tasks, and treat the high-level layers as taskspecific layers to learn more discriminative patterns. This mode is the most popular framework in the deep learning community. The illustration of hard parameter sharing can be found in Figure 4 (left sub-figure). For the soft parameter sharing multi-task learning (as shown in Figure 4 (right sub-figure)), they train each task independently, but make the parameters between different tasks similar via the introduced regularization constrains, such as L2 distance [53] and trace norm [54].
- 深度学习里多任务学习往往分 硬|软 参数共享
- 硬参数共享共享一个backbone,后面接多任务
- 软参数共享几乎完全独立,通过使不同任务中的参数相似(例如 L2-Distance, trace norm)来建立任务间的联系
- Multi-label Learning
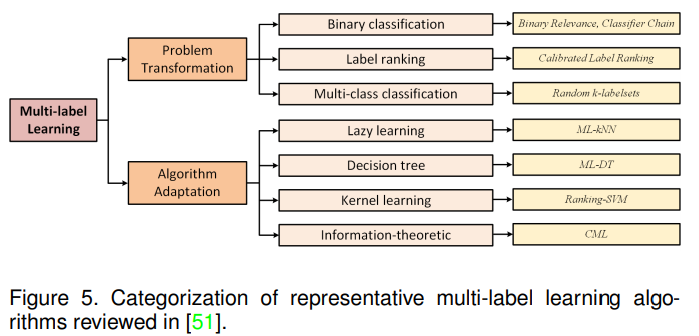
- problem transformation
- binary relevance algorithm
- 将问题转化为 后接多个二分类 的分类问题
- 简单,符合直觉
- 忽略了标签间的关联关系
- classifier chain algorithm
- 将问题转化为 二分类链 问题,每一个二分类结果以来之前的结果
- calibrated label ranking algorithm.
- 将问题转化为 标签排序 问题
- random k-Labelsets algorithm
- 将问题转化为 多组标签 分类问题
- binary relevance algorithm
- algorithm adaptation
- multi-label k-nearest neighbour
- multi-label decision tree
- ranking support vector machine Rank-SVM
- collective multilabel classifier
APPLICATIONS
- Visual attributes can be seen as a kind of mid-level feature representation which may provide important information for high-level human related tasks, such as person re-identification [128], [129], [130], [131], [132], pedestrian detection [133], person tracking [134], person retrieval [135], [136], human action recognition[137], scene understanding [138]. Due to the limited space of this paper, we only review some works in the rest of this subsections.
- 视觉属性可以视作一种中间等级的特征,可以用来协助高级的与人相关的任务,例如 re-id 行人检测 行人跟踪 行人回复 行人动作识别 场景理解等。此外,行人属性也作为一种标签用于统计单体和群体的画像,在商业场景下用途广泛
Algorithm
Global Image-based Method
ACN
- paper Person Attribute Recognition with a Jointly-trained Holistic CNN Model
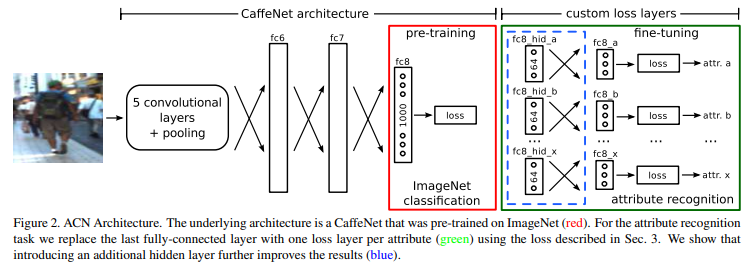
- they adopt a pre-trained AlexNet as basic feature extraction sub-network, and replace the last fully connected layer with one loss per attribute using the KL-loss.
- In addition, they also propose a new dataset named as PARSE-27k to support their evaluation. This dataset contains 27000 pedestrians and annotated with 10 attributes. Different from regular person attribute dataset, they propose a new category annotation, i.e., not decidable (N/A). Because for most input images, some attributes are not decidable due to occlusion, image boundaries, or any other reason.
- 最早期的文章之一,想法简单直接,推出了新的数据集PARSE-27k用做评估
DeepSAR/DeepMAR
- paper Multi-attribute Learning for Pedestrian Attribute Recognition in Surveillance Scenarios
- git https://github.com/dangweili/pedestrian-attribute-recognition-pytorch
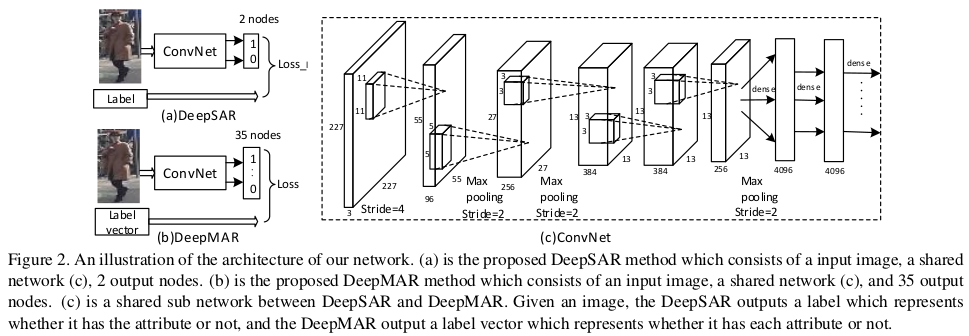
- Single Attribute Recognition (SAR)
- DeepSAR model is proposed to recognize each attribute one by one.Treating each attribute as an independent component, the DeepSAR method is proposed to predict each attribute.
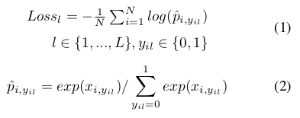
- Multi-attribute Recognition (MAR)
- To better utilize the relationship among attributes, the unified multi-attribute jointly learning model (DeepMAR) is proposed to learn all the attributes at the same time.
- Different from DeepSAR, the input of the DeepMAR is an image with its attribute label vector and the loss function considers all the attributes jointly.
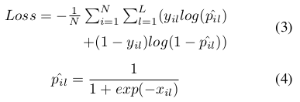
- Experiment
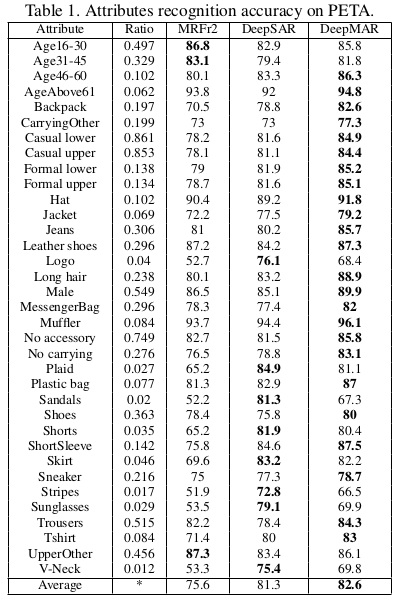
- 属性间的关联关系有助于提升平均准确率,但在具体各项上,有提升的有下降的
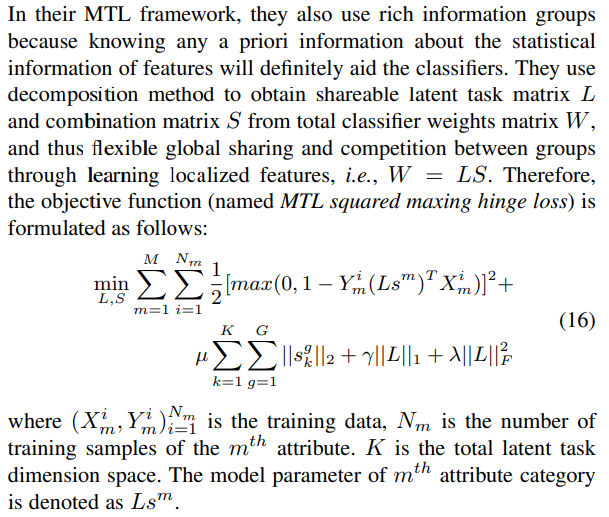
MTCNN
- paper Multi-task CNN Model for Attribute Prediction
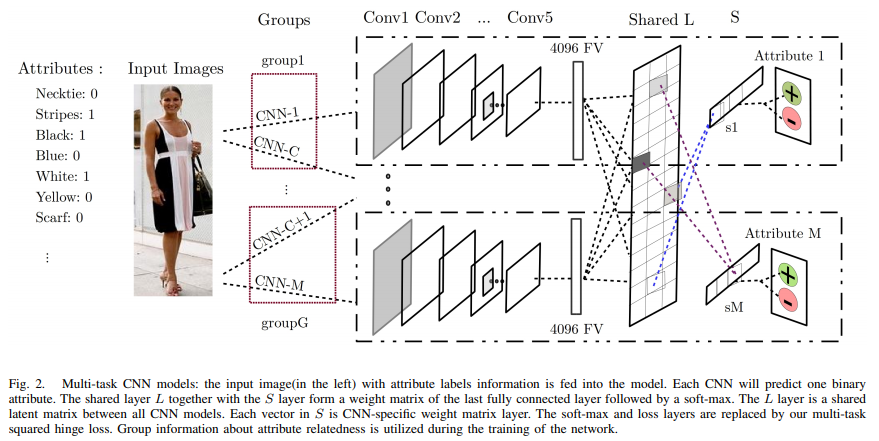
- Because our model requires more than one CNN model, we remove the last fully connected layers, as we substitute these layers with our own joint MTL objective loss, depending on the weight parameter matrix learned within.
- 移除原始网络最后一层的fc,使用了都有独特的 joint MTL objective loss 来联合训练
- Feature Sharing and Competition in MTL
Attention-based Method
HydraPlus-Net
- paper HydraPlus-Net: Attentive Deep Features for Pedestrian Analysis
- git https://github.com/xh-liu/HydraPlus-Net
- 提出了PA-100K
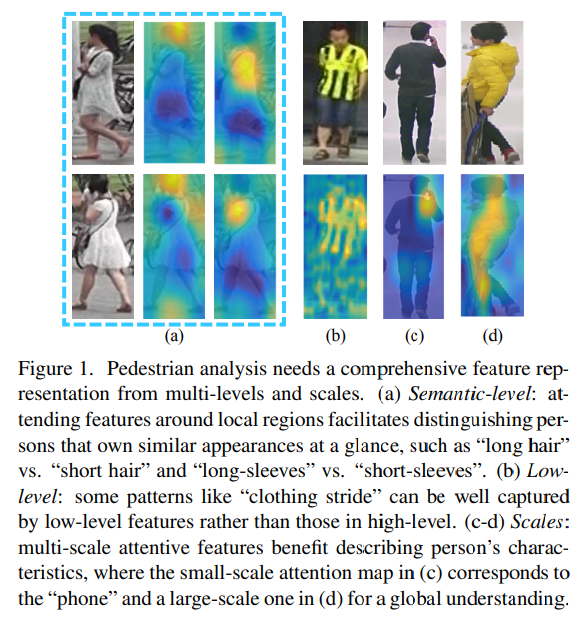
- 在行人分析里,不同的分析对象所需要的特征级别不同,尺度不同
- 语义级 不同人之间有所区分,但是咋看上去还挺相似例如 长头发vs短头发 长袖vs短袖
- 低层级 例如 clothing stride 就可以很好地在低层特征算出,比高层算出的结果要好
- 尺度差异 有些任务的关注点在手部而有些是全身,尺度变化大
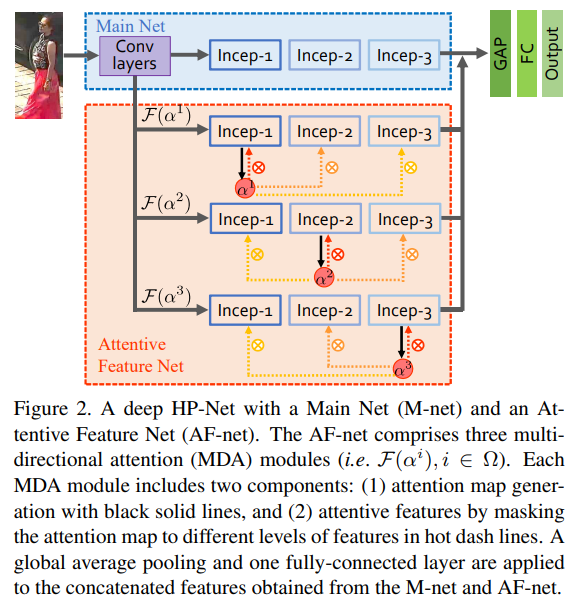
- 由 MainNet AttentiveFeatureNet 构成,由MNet生成特征由AFNet生成attention mask,其中F函数对应的incept模块是MNet中三个incept模块的复制(MNet会先被预训练,主体是当年流行的inception-v2)
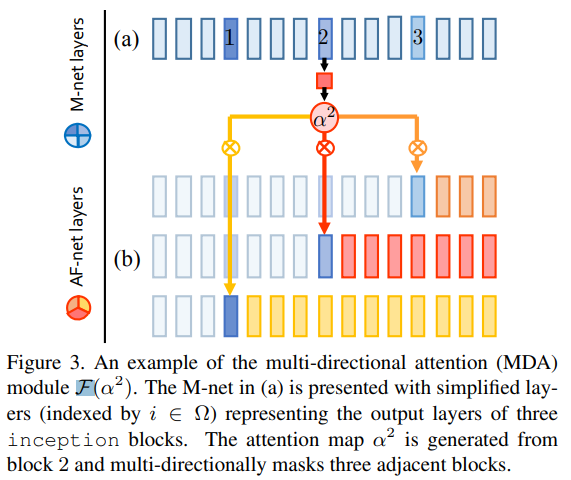
- 一个MDA的例子,对于每一个在MNet中的incept模块,通过和三层incept的相互关联得到新的结果
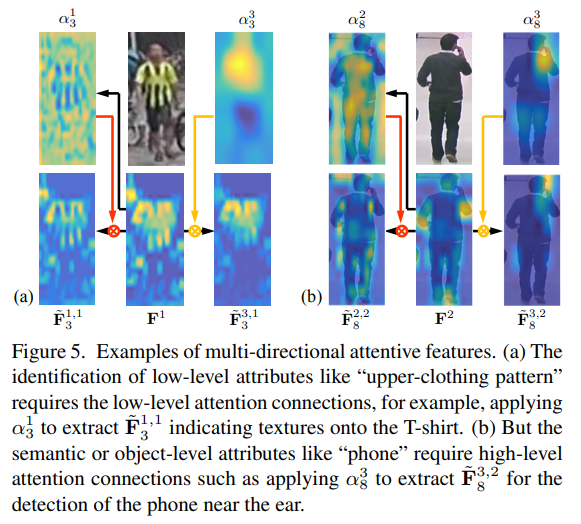
- 举个例子如上图所示,原始输出结果结合毗邻特征,结合低层特征就变得更加惊喜噪音也更多,结合高层特征整体更加突出完整信息也变少更集中,对于不同的任务可以各取所需
VeSPA
- paper Deep viewsensitive pedestrian attribute inference in an end-to-end model
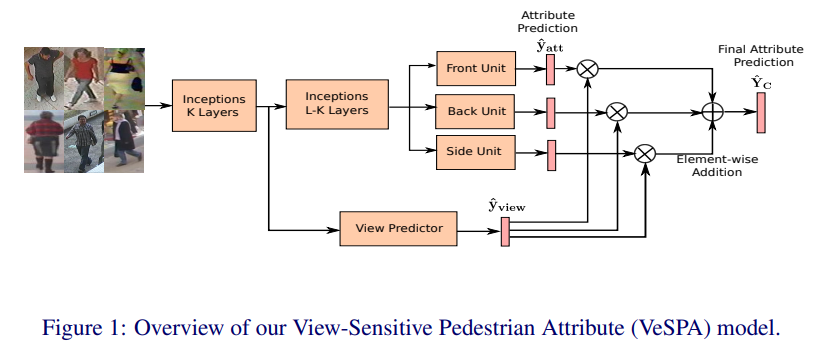
- We adapt a deep neural network for joint pose and multi-label attribute classification. The overall design of our approach is shown in Figure 1. The main network is based on the GoogleNet inception architecture [20]. As shown, the network contains a view classification branch and three view-specific attribute predictor units. The view classifier and attribute predictors are both trained with separate loss functions. Prediction scores from weighted view-specific predictors are aggregated to generate the final multi-class attribute predictions. The whole network is a unified framework and is trained in an end-to-end manner.
- 只要使用了GoogleNet inception architecture
- 分成了正面 背面 侧面三个分支预测属性
- 引入额外分支用于分类是正面背面侧面,并将其分值分别乘在三个分支上,最终综合得到最后结果
- 这里引入了front back side,下面引用一张图说明

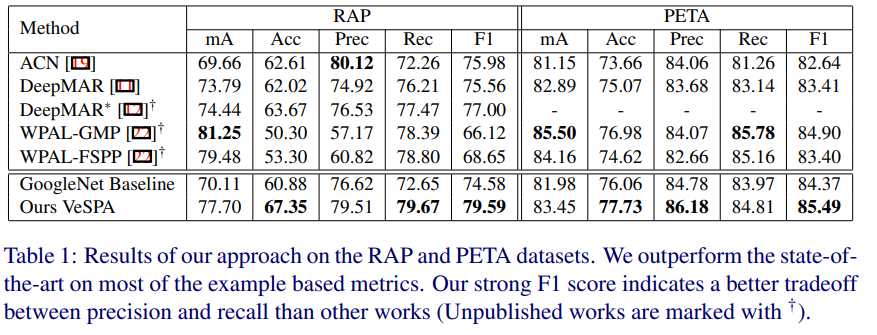
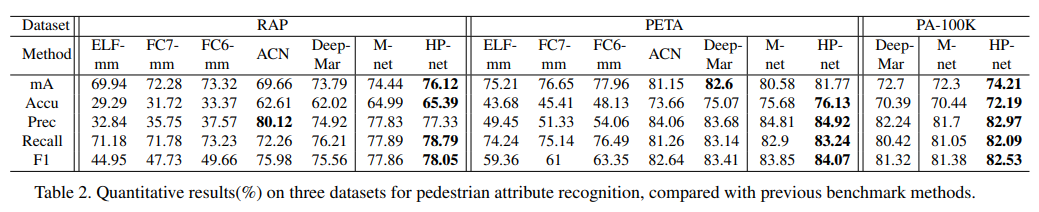
- 从结果上看效果很理想,甚至超过了花里胡哨的HPNET
DIAA
- paper Deep Imbalanced Attribute Classification using Visual Attention Aggregation
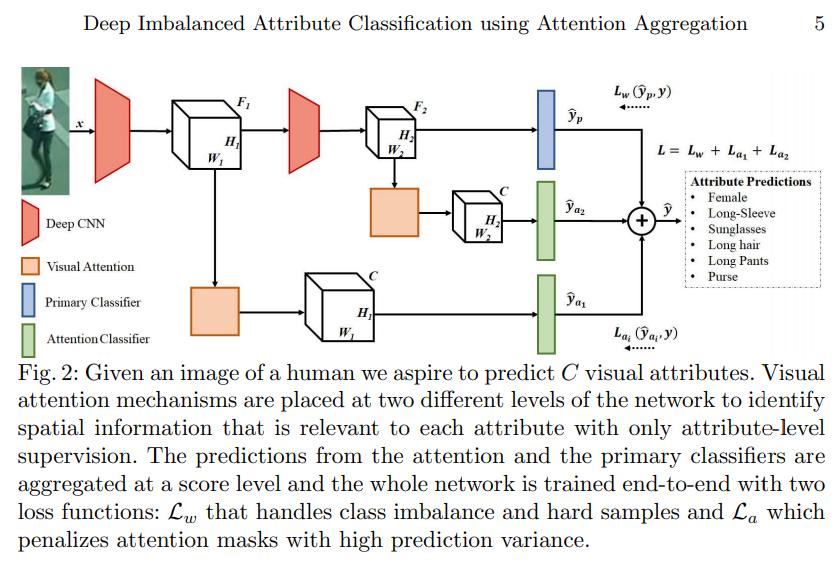
- 简单直接,且看看具体有什么不同
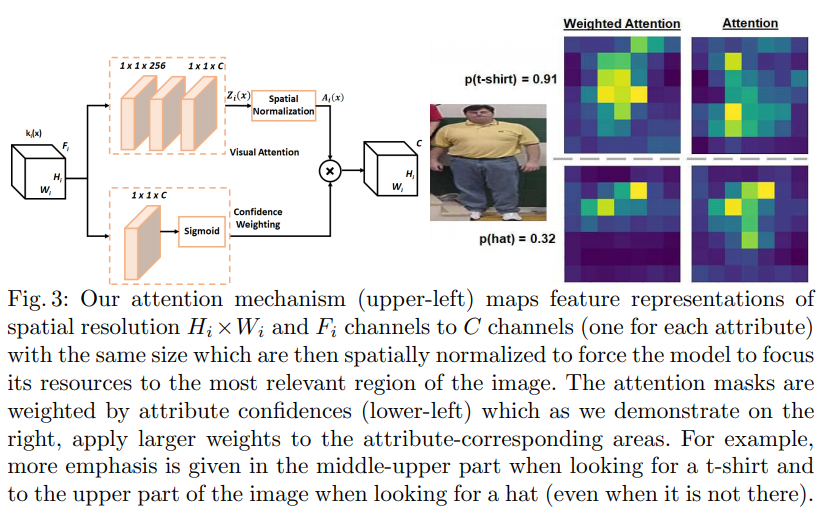
- 特殊的attention机制,一边是sigmoid的权重层,另一边是常规卷积层加上空间的正则化
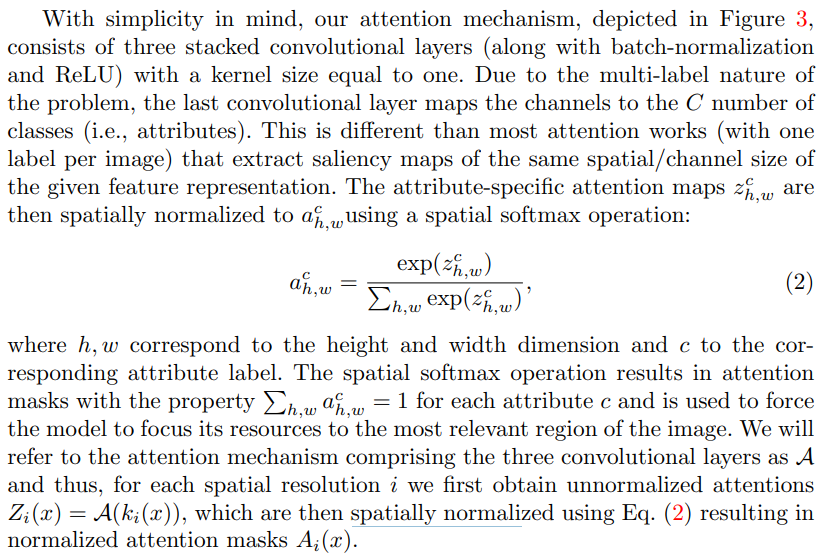
- 通过spatial softmax达到单层的normalization,结果在iv中展示,确实能使attention更集中了

- 和focal loss的变种,其中Wc被设定为与类别属性分布相关的权重值,是每一类不同的,作者称其为 Deep Imbalanced Classification
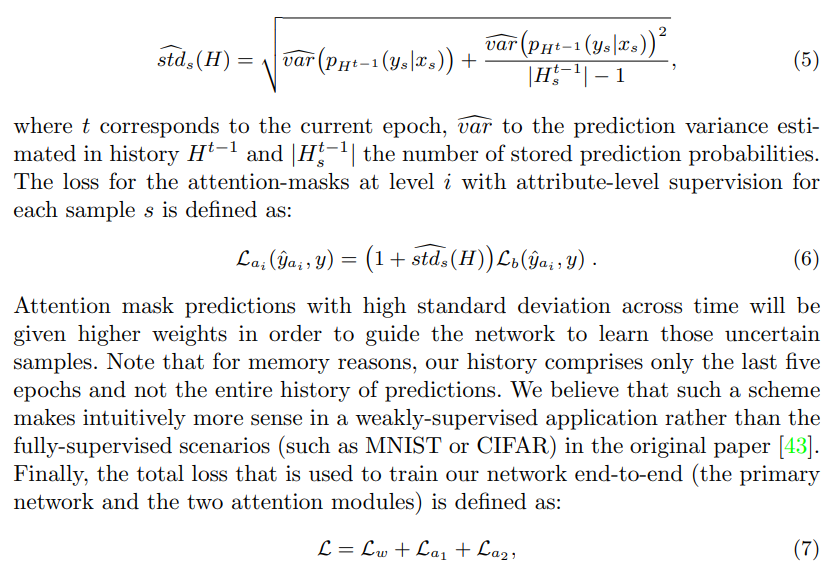
- 对于非主分支的两个分支使用了常规的分类loss,并记录前值计算标准差作为系数加大loss
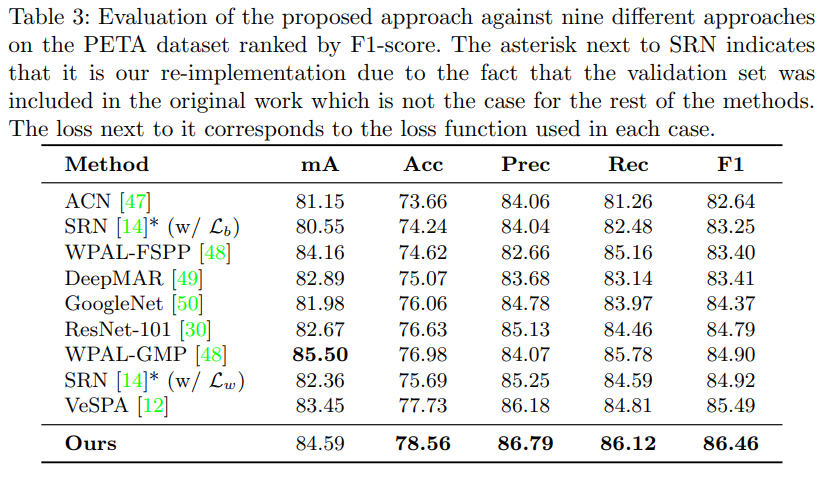
- PETA上实验结果比较理想
CAM
- paper Human attribute recognition by refining attention heat map
- git https://github.com/hguosc/Human-attribute-recognition-by-refining-attention-heat-map
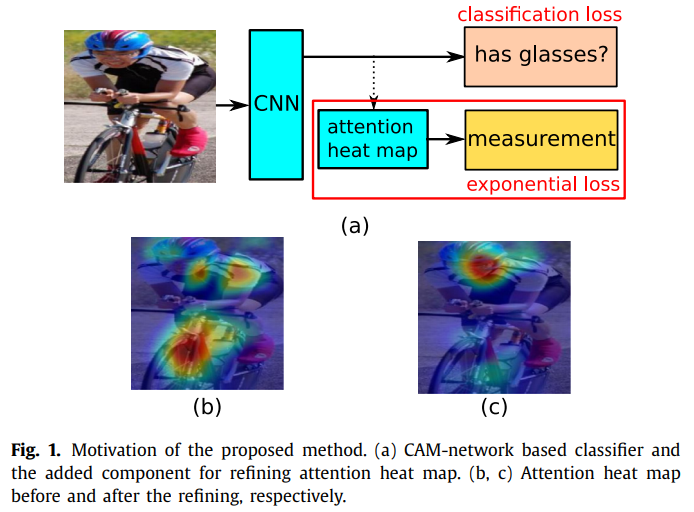
- 展示了效果
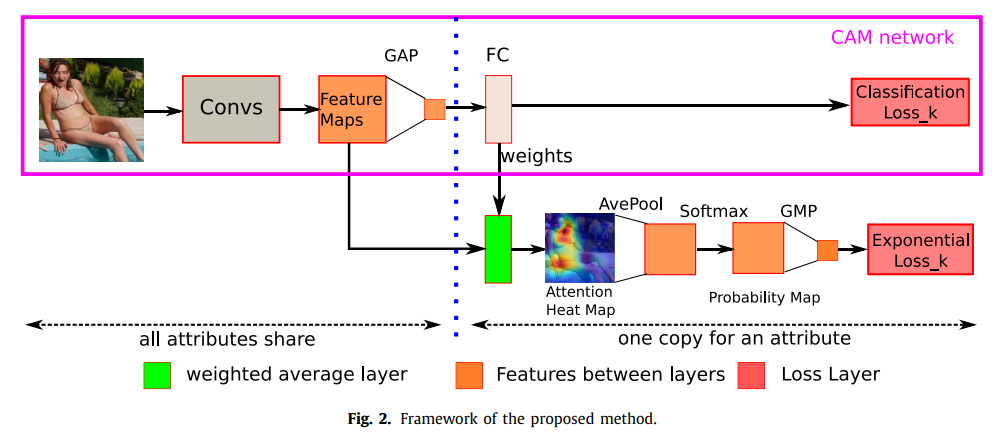
- 在backbone各attribute共享,在FC开始分离,通过weight average layer(The customization of the weighted average layer is used to embed the attention heat map into the network training and the modification of the fully-connected layer is used to output both features and weights.)处理得到attention map,继续常规操作得到结果

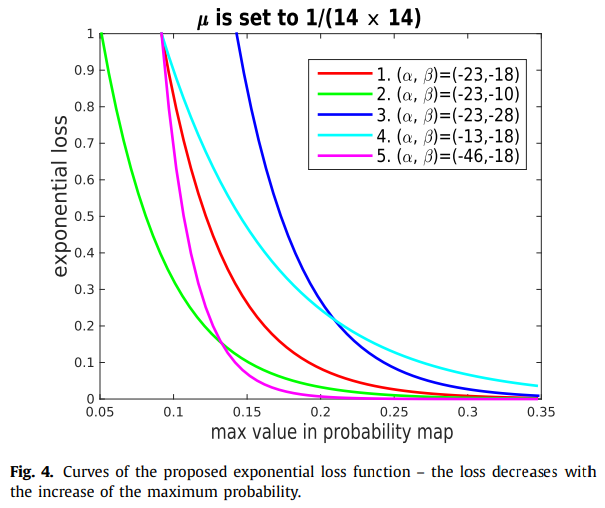
- 可见这个exponential loss主要是为了使最大值更大,使关注点更集中
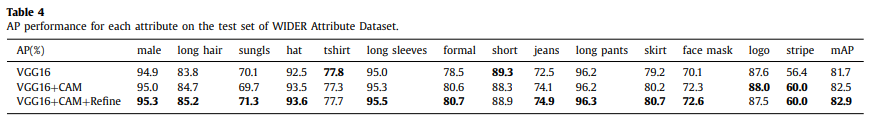
- 只有 wider 的结果,较baseline有所提升
Curriculum Learning Method
MTCT
- paper Multi-Task Curriculum Transfer Deep Learning of Clothing Attributes
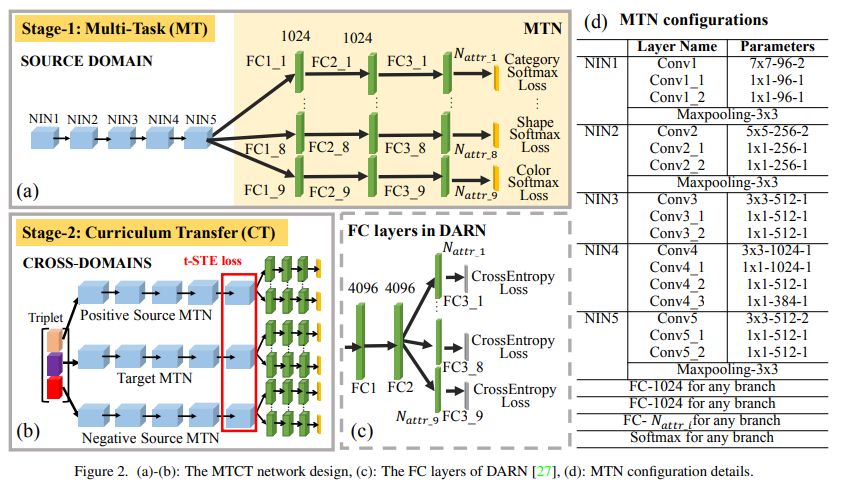
- 训练分两个阶段,一阶段是常规的属性学习MTN,使用常规的分类loss;第二阶段将一阶段训练完成的MTN重新构建成为三元组,使用e t-distribution Stochastic Triplet Embedding (t-STE) loss进行训练
- 文章不是针对行人属性的,不做拓展
CILICIA
- paper Curriculum learning for multi-task classification of visual attributes
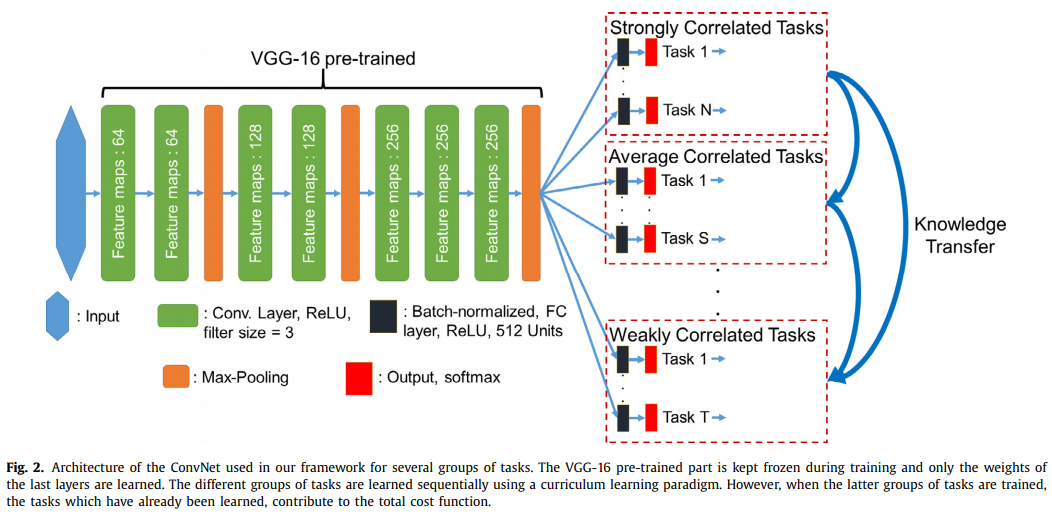
- 这篇文章的主要思想就是先学习得到task间的相关性,然后定义下个阶段的task组,循环学习到只有2个任务
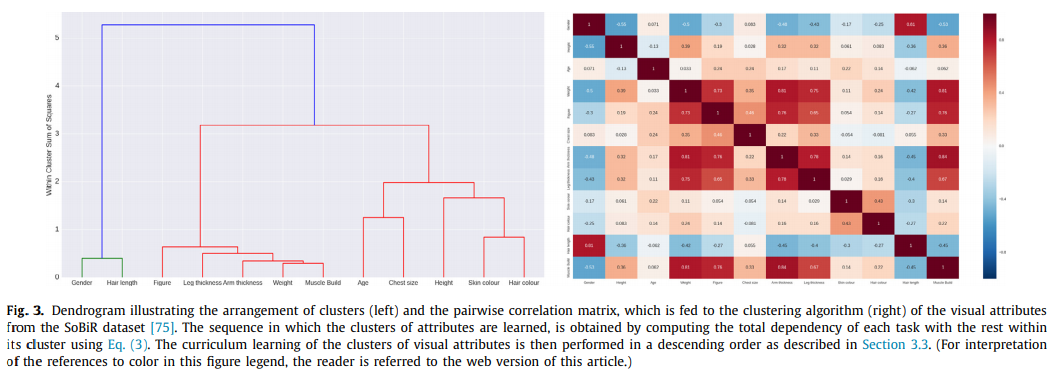
- 类似这样,是多stage的做法,不是现在的主流
Graph based Method
DCSA
- paper Describing clothing by semantic attributes
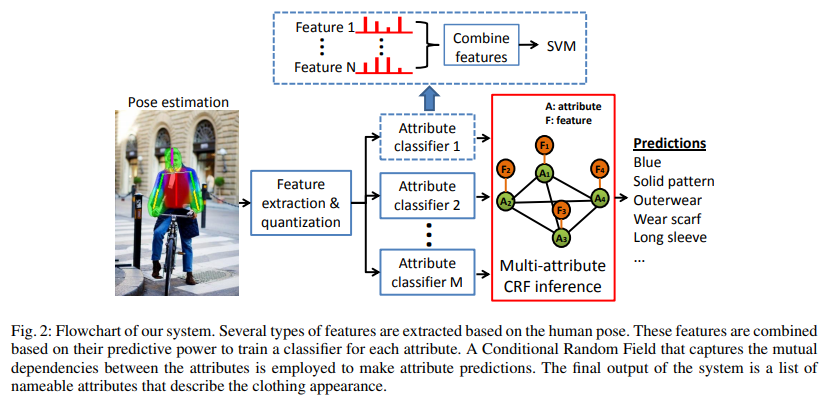
- 整体的思路即使放在现在也不过时,12年的文章。先通过pose estimation得到大致的区域,然后划分区域特征抽取,得到各属性分类结果,然后构建多属性图使用CRF进行推论得到结果。具体方法如SIFT SVM等已不适用现在,不展开
A-AOG
- paper Attribute and-or grammar for joint parsing of human pose, parts and attributes
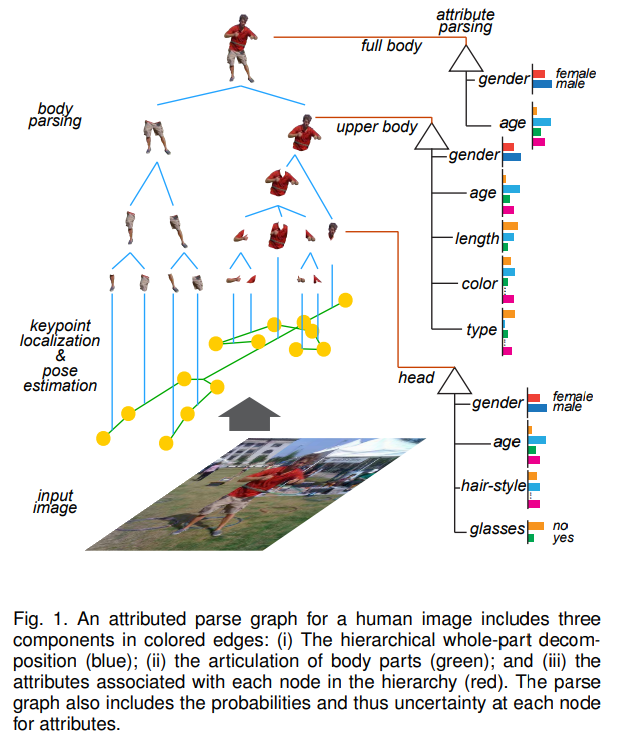
- 人体分割,按约定的树构建层级关系,各部位分别出各自的属性,效果很炫酷
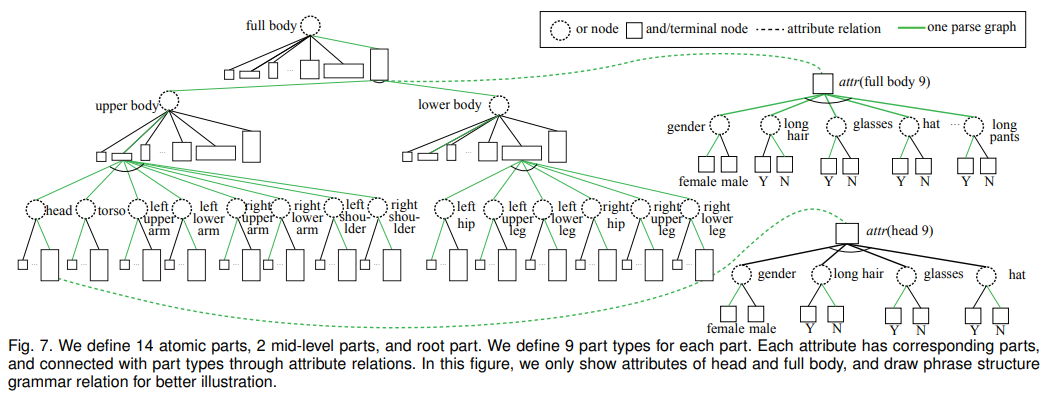
- 低层组件定义了14个,中间件2个,root件一个。每个部件拥有9个相关属性,通过属性关联链连接各部分属性。
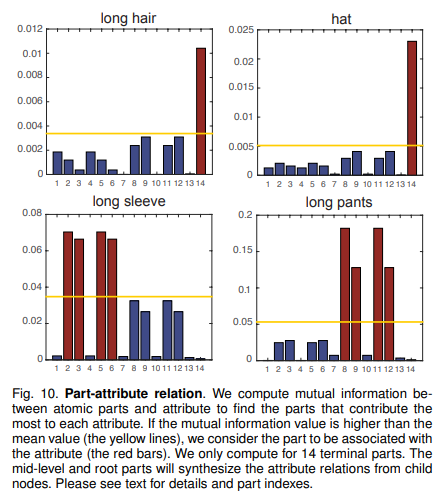
- 如果结果理想的话,单个属性会被某几个部分突出地代表
- 本文对于loss只是一句 CE 带过,整体结果也没有在常见的数据集上,只有思路供参考
PAR w/ GCN
- paper Multi-Label Image Recognition with Graph Convolutional Networks
- git https://github.com/2014gaokao/pedestrian-attribute-recognition-with-GCN
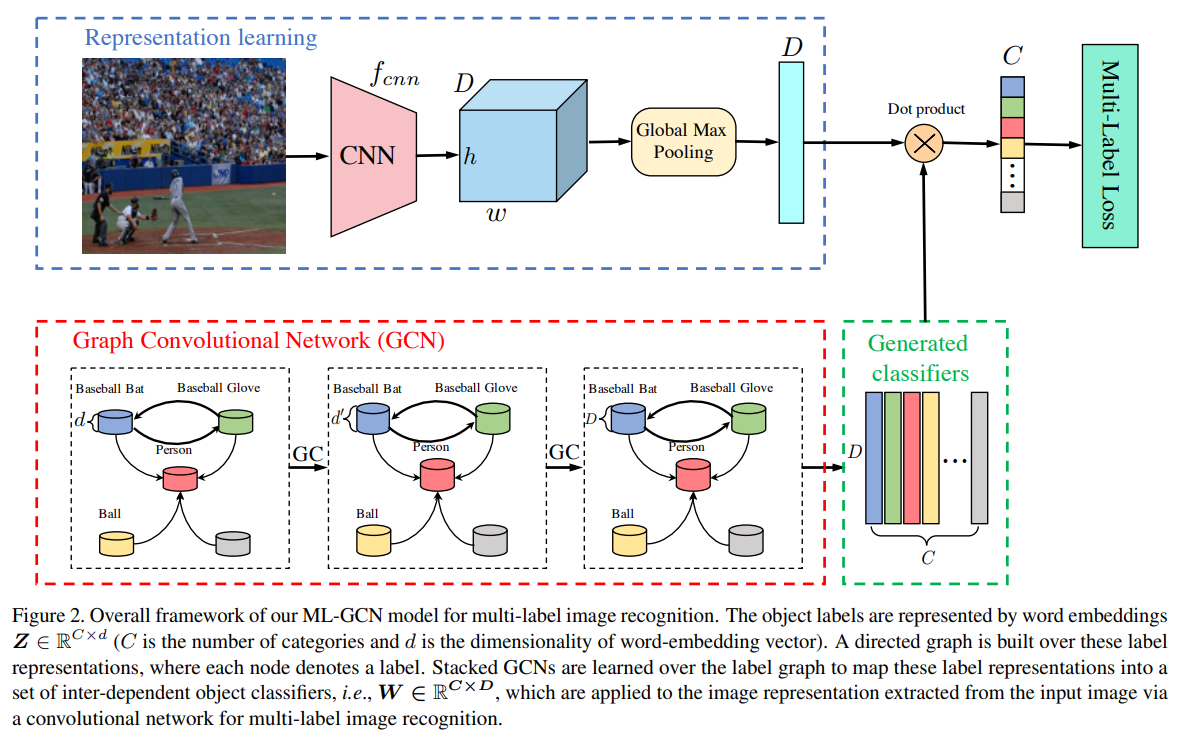
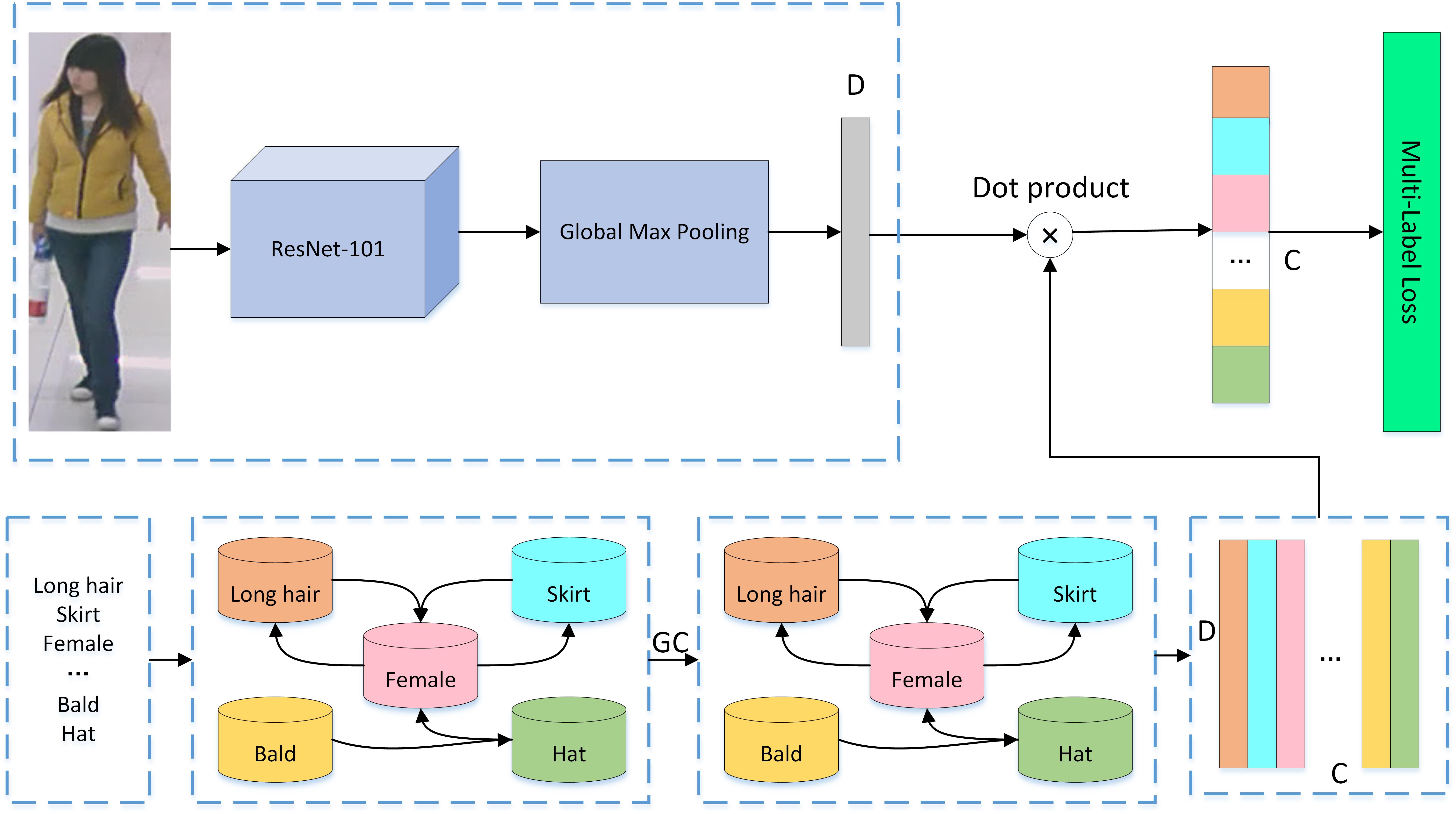
- b图是原始论文网络框架图,c图是git项目的图,原理是相同的。上面分支是backbone出特征,下面是GCN分支出关联关系,点乘得到结果。那么这个GCN的输入输出是什么呢?究竟完成了一个什么事情?
- 理解GCN 推荐 https://www.zhihu.com/question/54504471/answer/332657604
- 介绍下GCN代码和glove
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41# GCN方法,通过矩阵乘改变输出维度
class GraphConvolution(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, bias=False):
super(GraphConvolution, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(in_features, out_features))
if bias:
self.bias = Parameter(torch.Tensor(1, 1, out_features))
else:
self.register_parameter('bias', None)
self.reset_parameters()
def reset_parameters(self):
stdv = 1. / math.sqrt(self.weight.size(1))
self.weight.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
if self.bias is not None:
self.bias.data.uniform_(-stdv, stdv)
def forward(self, input, adj):
support = torch.matmul(input, self.weight)
output = torch.matmul(adj, support)
if self.bias is not None:
return output + self.bias
else:
return output
def __repr__(self):
return self.__class__.__name__ + ' (' \
+ str(self.in_features) + ' -> ' \
+ str(self.out_features) + ')'
# GLOVE其实指的是 原始label word2vec 后得到的库,文章里称glove
word_to_ix = {j: i for i, j in enumerate(select_name)}
embeds=nn.Embedding(60,300)
word2vec=torch.tensor([])
for i in range(len(select)):
lookup_tensor=torch.tensor([word_to_ix[select_name[i]]],dtype=torch.long)
embed=embeds(lookup_tensor)
word2vec=torch.cat((word2vec,embed),0) 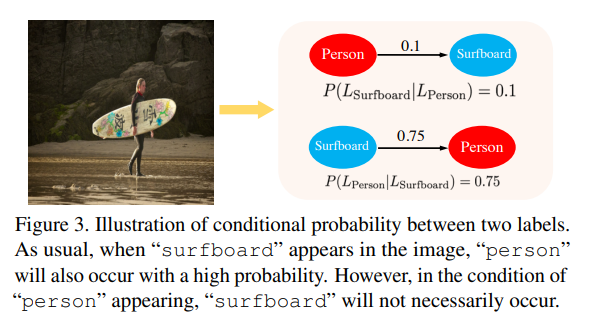
- 这张图说明了GCN想要的结果,主要是想要这个条件概率。以下是adj的初始化方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33# 初始化
for idx in partition['train'][0]:
t=np.array(dataset['att'][idx])[dataset['selected_attribute']]
for i in range(len(np.array(dataset['att'][idx])[dataset['selected_attribute']])):
if t[i]==1:
for j in range(len(np.array(dataset['att'][idx])[dataset['selected_attribute']])):
if t[j]==1 and j!=i:
concur[i][j]+=1
# 初始化A norm化卡阈值 + 1 得到初始值
def gen_A(num_classes, t, adj_file):
import pickle
result = pickle.load(open(adj_file, 'rb'))
_adj = result['adj']
_nums = result['nums']
_nums = _nums[:, np.newaxis]
_adj = _adj / _nums
_adj[_adj < t] = 0
_adj[_adj >= t] = 1
#_adj = _adj * 0.9 / (_adj.sum(0) + 1e-6)
_adj = _adj + np.identity(num_classes, np.int)
return _adj
# 真实使用时,对应矩阵运算就是 D^(-1)AD
def gen_adj(A):
D = torch.pow(A.sum(1).float(), -0.5)
D = torch.diag(D)
adj = torch.matmul(torch.matmul(A, D).t(), D)
return adj
# adj其实指的是 adjacency matrix, 用于描述图节点的矩阵。预处理后使用 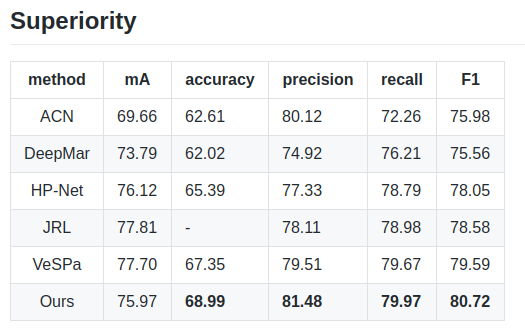
- rap的结果,原始论文不是拿来做这个用途没有相关的结果。从结果上看还是很顶的,基本达到了sota水平
VSGR
- paper Visua-semantic graph reasoning for pedestrian attribute recognition
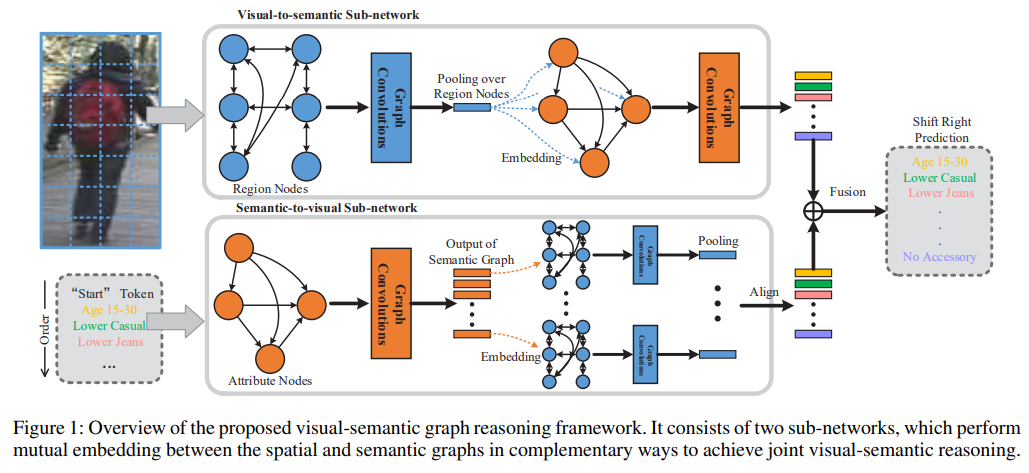
- Visual-to-semantic Sub-network + Semantic-to-visual Sub-network fuse得到结果
- 目前无开源代码,原文里操作多且复杂,难以非常清晰地理解
- Experiment
- 有待开源后进一步研究
Loss Function based Method
WPAL
- paper Weakly-supervised Learning of Mid-level Features for Pedestrian Attribute Recognition and Localization
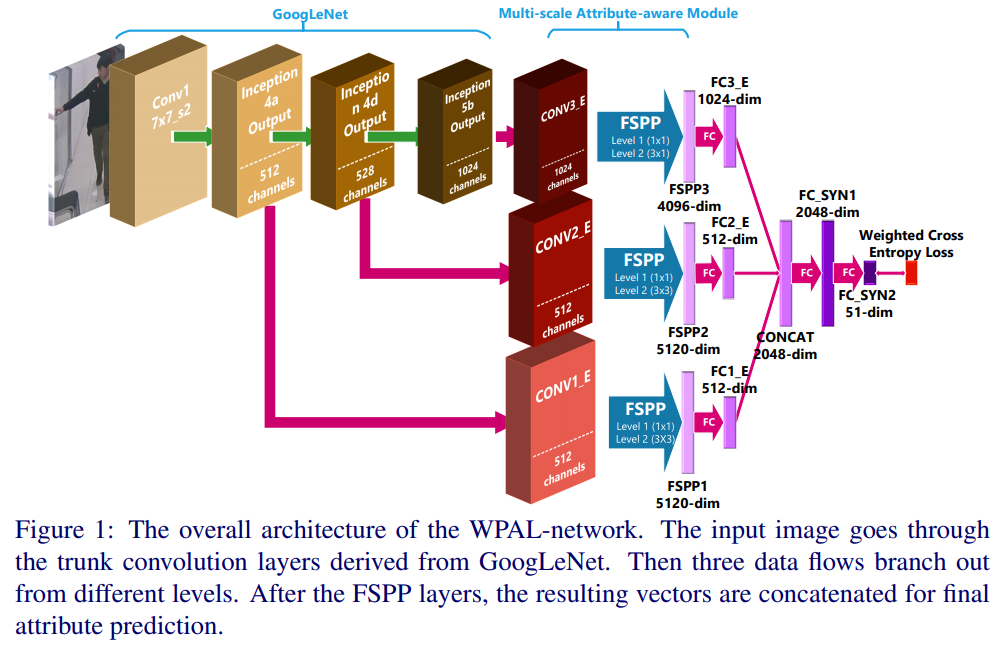
- 从结构上看主要的贡献是 multi-level feature + FSPP + weighted-CE(Flexible Spatial Pyramid Pooling )
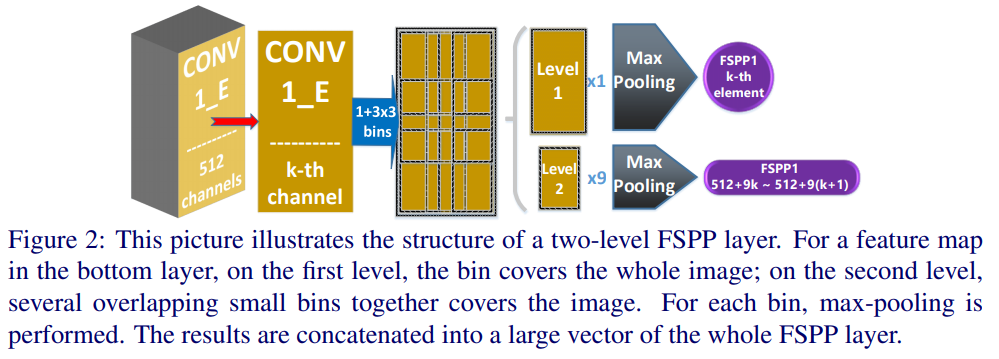
- level 1是全图的conv,level 2是用了预设的9个bins去框特征得到的结果
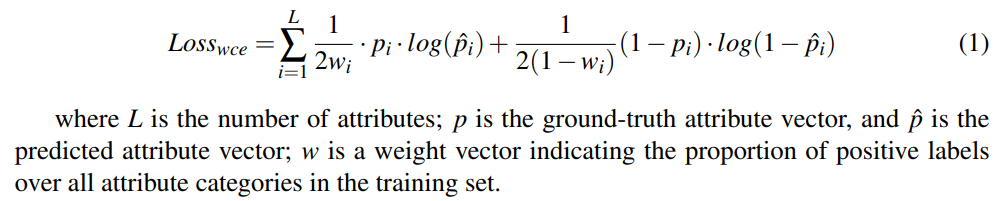
- Wi是label在数据集中相对数量的百分比,平衡数据

- 提出了新的衡量指标 IoP,然而并没有多少人用
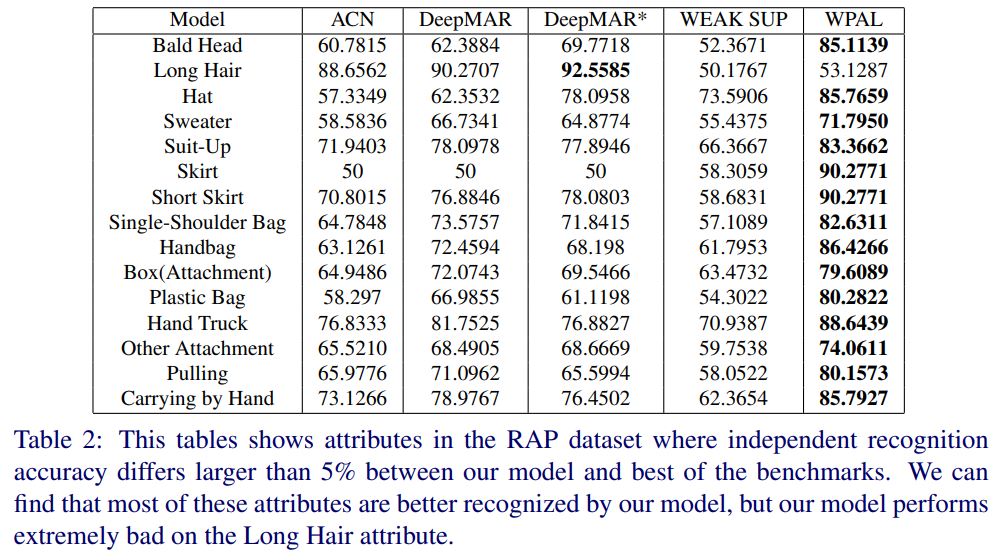
- 在RAP上表现不错,但是这个方法对头发极为不鲁邦
AWMT
- paper Adaptively weighted multi-task deep network for person attribute classification
- git https://github.com/qiexing/adaptive_weighted_attribute
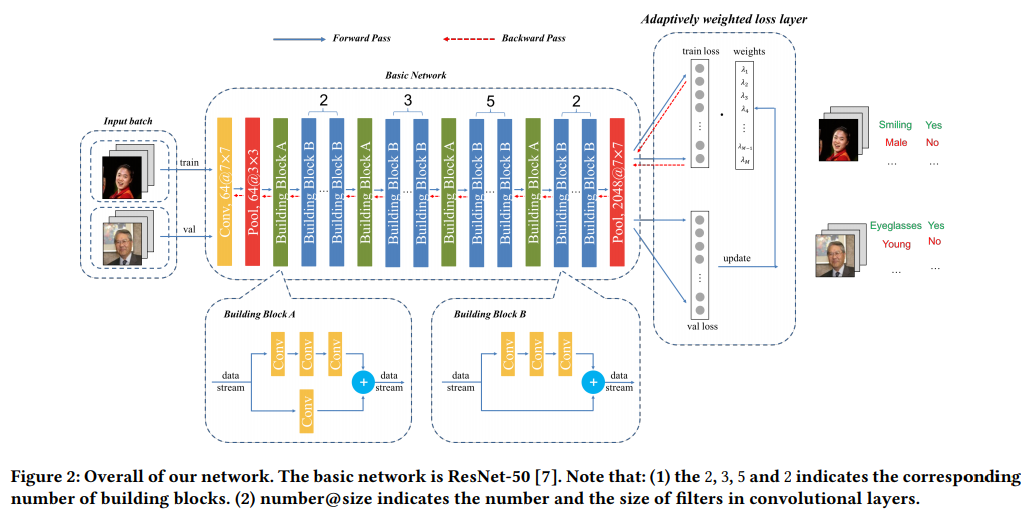
- 结构上只是常规的res50,输入同时有train和val,在loss上有所技巧
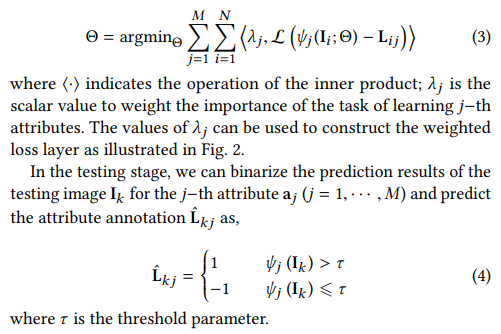
- 任务目标是使 Θ 最小,其中 λ 为可更新超参(权重),Lkj是阈值

- 主题算法一共有两个部分
- 输入 train val 进行forward,train_loss * λ 作为backward的loss; 权重λ在到达更新period时更新
- λ 的 更新方法
- 其实还是用了 val的数据,还间接参与了backward
Part-based Method
Poselets
- paper Describing People: A Poselet-Based Approach to Attribute Classification
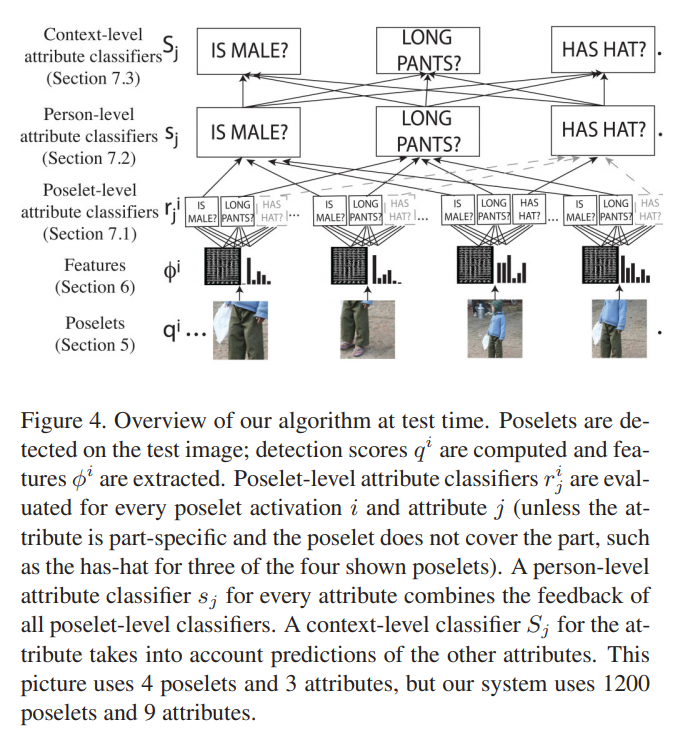
- 先使用poselets讲身体分为几张图
- poselet paper http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~cv-fall2012/slides/dinesh-paper.pdf
- We use the method of Bourdev et al. [3] to train 1200 poselets using images from the training and validation sets. Instead of all poselets having the same aspect ratios, we used four aspect ratios: 96x64, 64x64, 64x96 and 64x128 and trained 300 poselets of each. For each poselet, during training, we build a soft mask for the probability of each body component (such as hair, face, upper clothes, lower clothes, etc) at each location within the normalized poselet patch (Figure 5) using body component annotations on the H3D dataset [4].


- 后接3个SVM用于分类
RAD
PANDA
- paper PANDA: Pose Aligned Networks for Deep Attribute Modeling
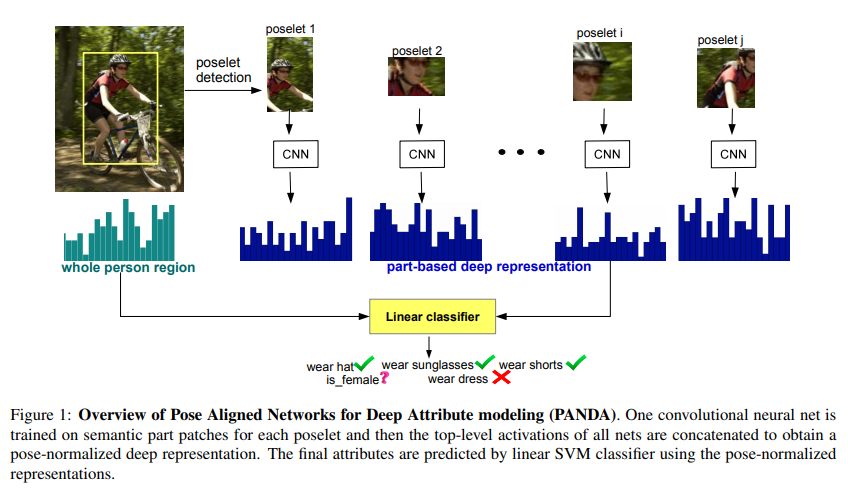
- 与Poselets很相似,但是有了独立的CNN支持
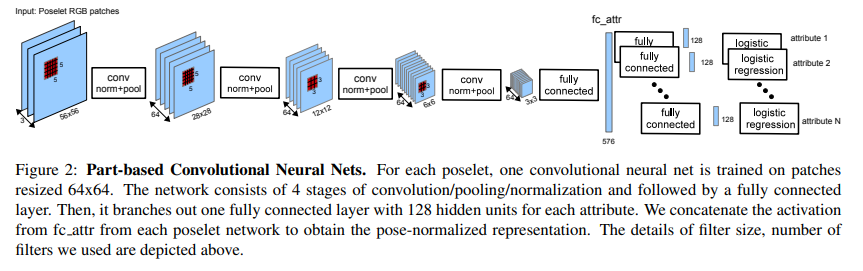
- 在有独立CNN支持后性能改善较多
MLCNN
- paper Multi-label CNN Based Pedestrian Attribute Learning for Soft Biometrics
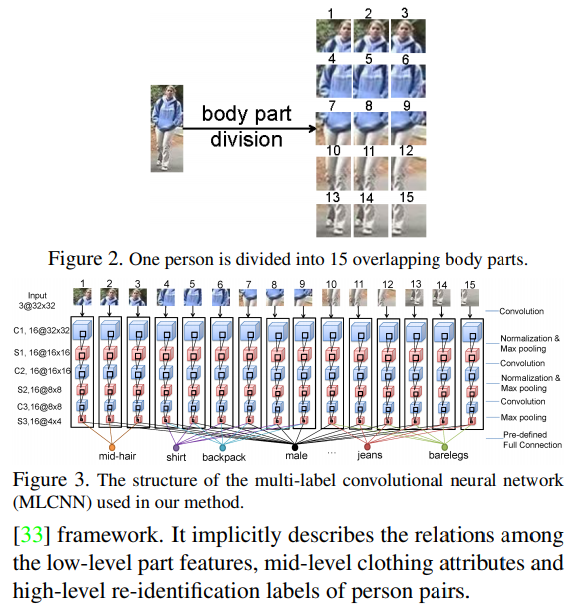
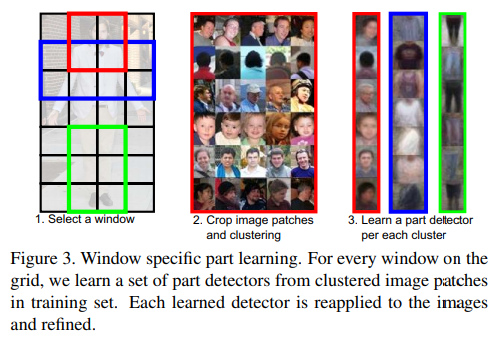
- 直接把一张图划分为有overlap的15个块,对不同的块进行卷积操作,使用特定块结果得到特定标签结果,如mid-hair标签使用了1,2,3块。
AAWP
- paper Actions and Attributes from Wholes and Parts
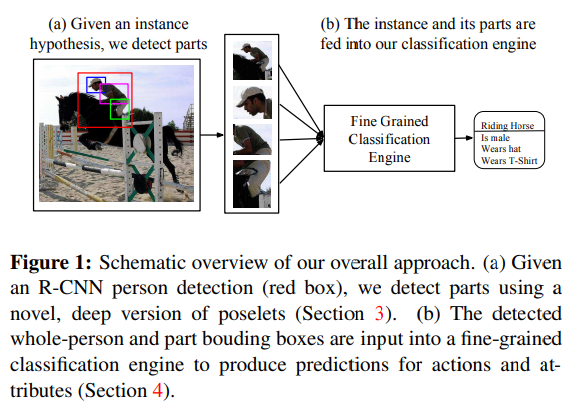
- 这篇文章开始使用 R-CNN 检测,从图像中得到 全身,头部,上身,下身 的具体位置,切割出来进行属性识别
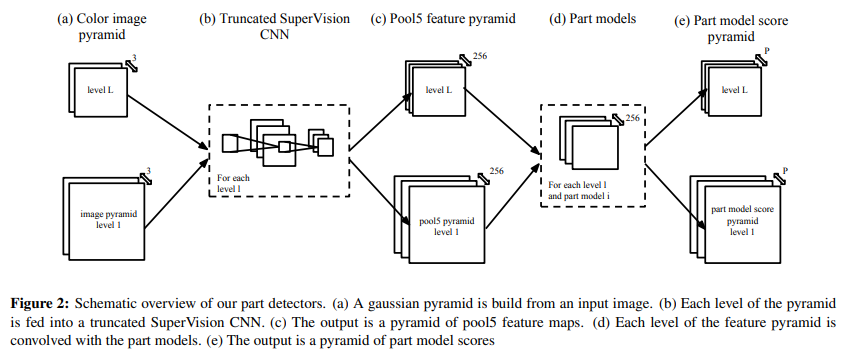
- 对检测部分,使用高斯金字塔处理过的图像作为输入,通过多尺度提高结果,已经非常类似与FPN
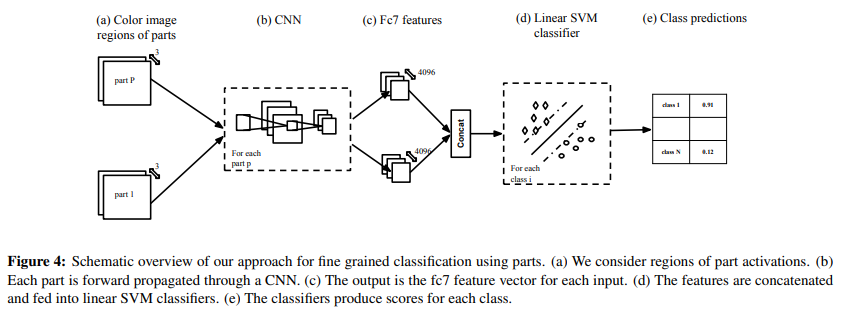
- 分类器还是很普通的 CNN + SVM 的做派
ARAP
- paper Attribute Recognition from Adaptive Parts
- 通过关键点得到各部件,然后得到各部分属性
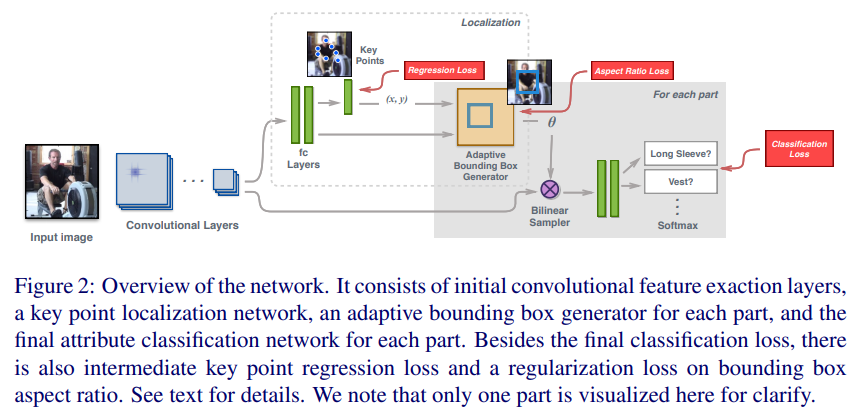
- 关键点检测和属性识别共享基础backbone,先进行关键点检测,得到感兴趣的部件区域,将特征层上采样与部件区域对其,最后fc分类得到结果

- 值得一提的是,作者不仅对关键点设置了回归loss,也对bbox的结果进行了 loss 约束,虽然形式有些怪异,不过确实改进了性能
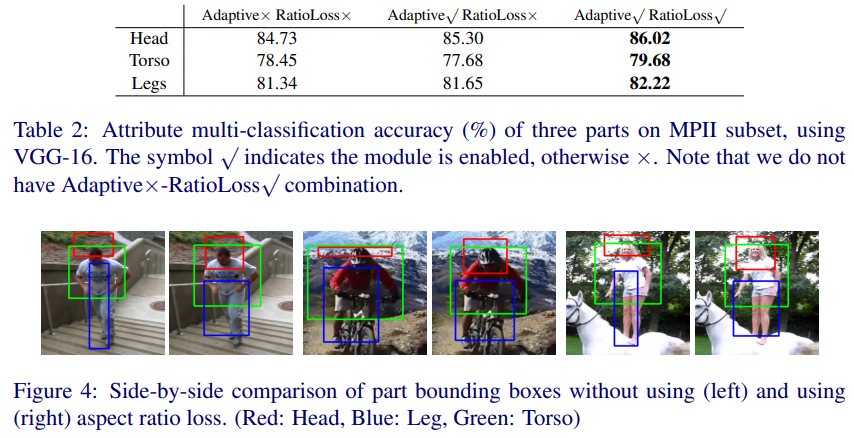
- 毫无疑问的是,精准定位会带来的属性识别性能提升,尤其是ratio loss带来的对bbox的修正使整体方法更完整
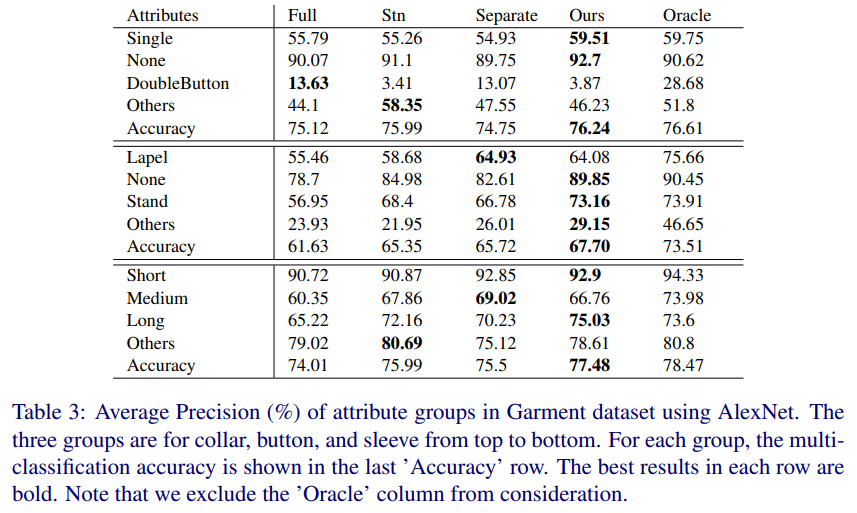
DeepCAMP
- paper Deepcamp: Deep convolutional action & attribute mid-level patterns
- 看着这个示意图青一块紫一块的,其实是 聚类(cluster) 的结果,继续往下看
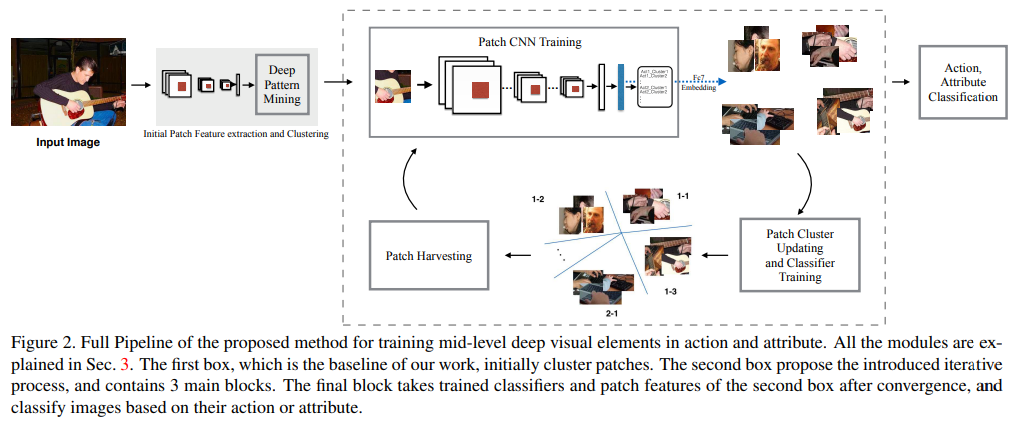
- 不同于后来的基于attention的无监督注意力机制,本文使用了聚类方法,对各patch特征进行无监督处理
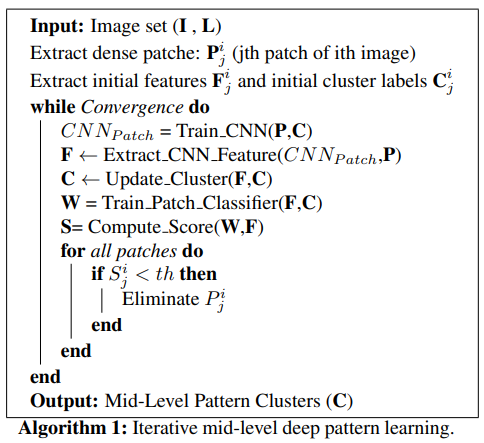
- 伪代码简单明了很清晰,先抽特征,更新聚类器,得到分值,最后得到结果。值得一提的是,本文使用了LDA作为降维聚类工具
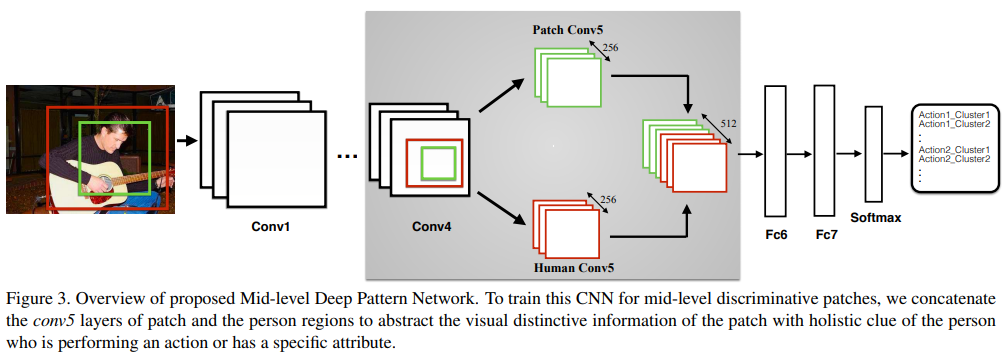
- Mid-level Deep Patterns Network 具体如上图所示,图上没有标出的是作者使用了fast-RCNN,在conv4后面是roipooling层,对两个关注的patch点及整个人进行roipooling,concat后得到结果
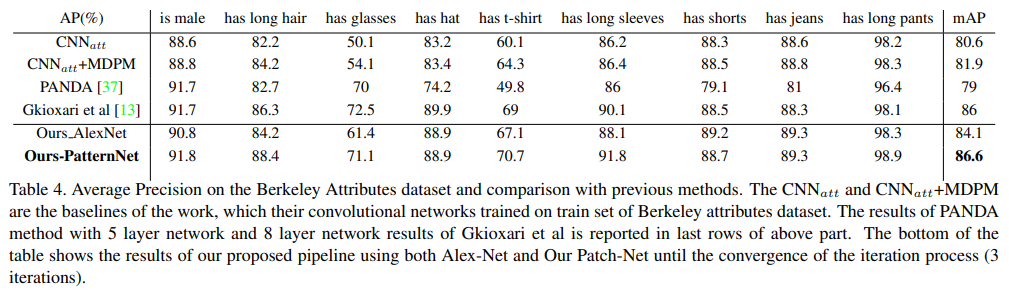
- 大幅超过了PANDA
PGDM
- paper POSE GUIDED DEEP MODEL FOR PEDESTRIAN ATTRIBUTE RECOGNITION IN SURVEILLANCE SCENARIOS
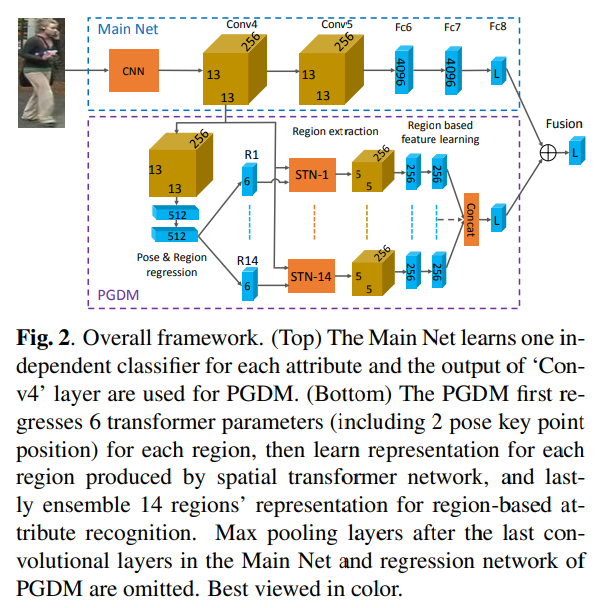
- 整体思路和16年的ARAP基本一致,在网络设计上做了改进
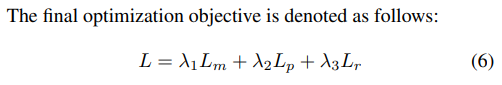
- Lm:MainNet分类loss*热力weight
- Lr:关键点回归smooth-l1loss
- Lp:fuse后分类loss
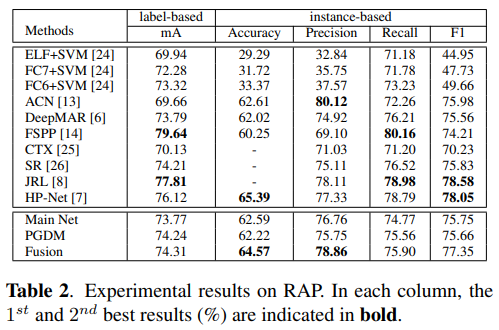
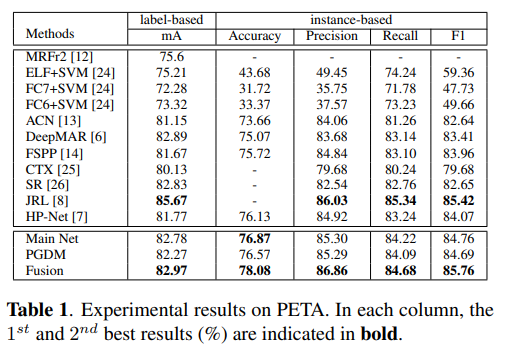
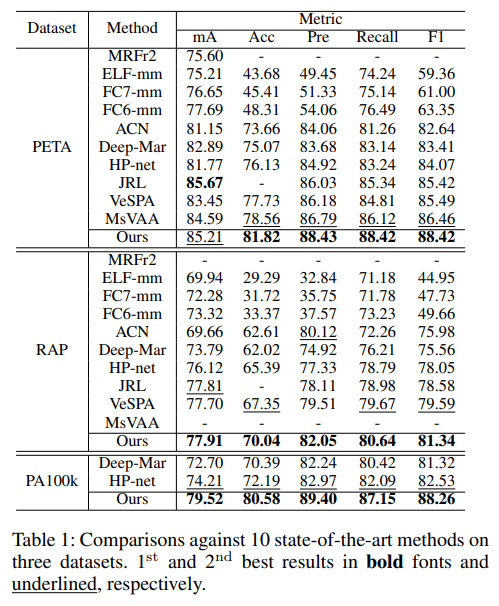
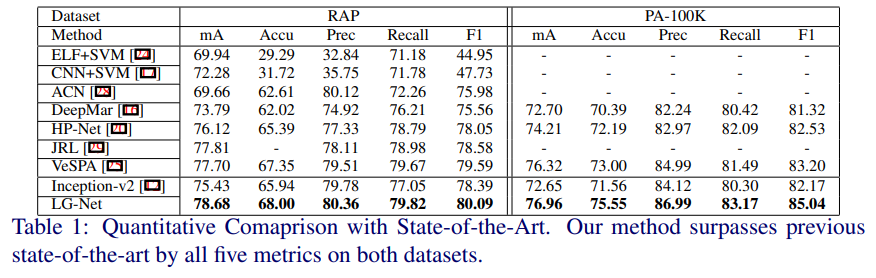
- 展示了PETA RAP上对HP-Net的全方位压制
DHC
- paper Human Attribute Recognition by Deep Hierarchical Contexts
- 发布了 WIDER Attribute dataset,多人多属性数据集
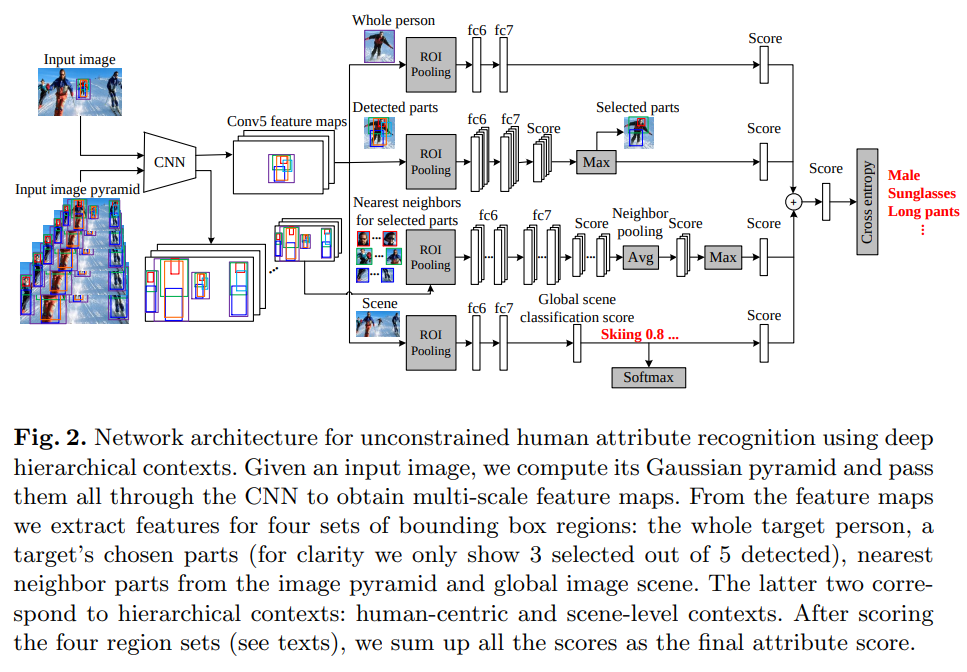
- 对于一张input,将其经过高斯金字塔处理,一起送入网络。得到 1.目标人整体 2.目标人各部分检测 3.多尺度各部件近邻特征 4.全图
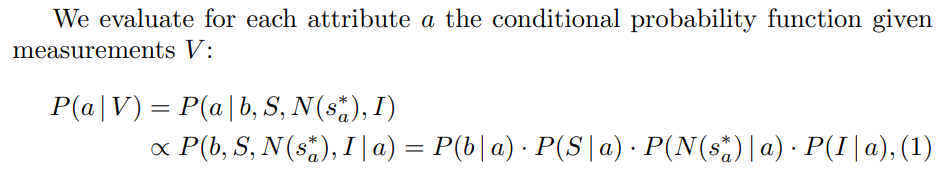
- 连乘概率得到最终结果
LGNet
- paper Localization guided learning for pedestrian attribute recognition
- git https://github.com/lpzjerry/Pedestrian-Attribute-LGNet
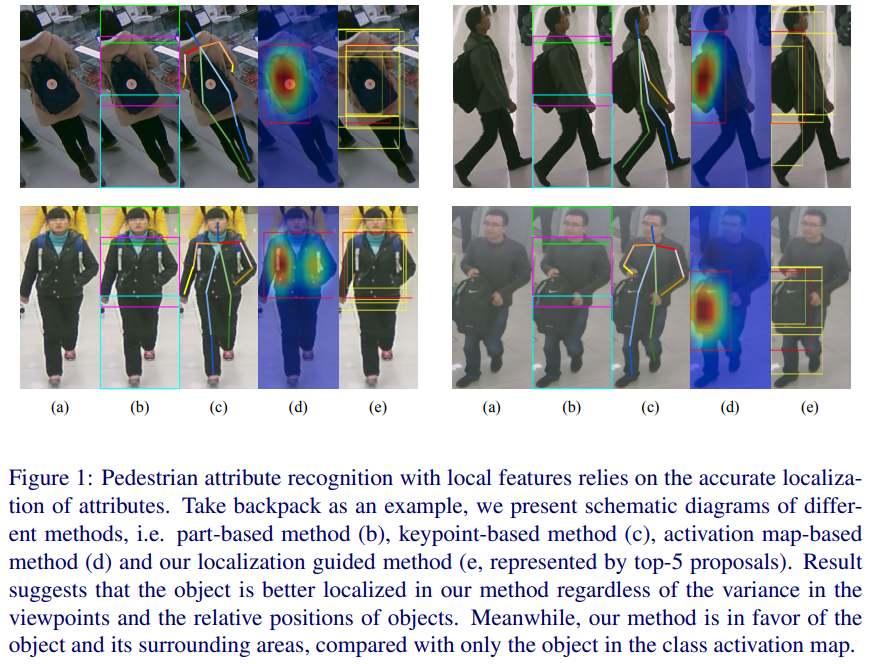
- 介绍地很好,a.原图 b.按预设模板直接分块干 c.基于关键点 d.激活图方法(类似attention) e.依赖定位的方法
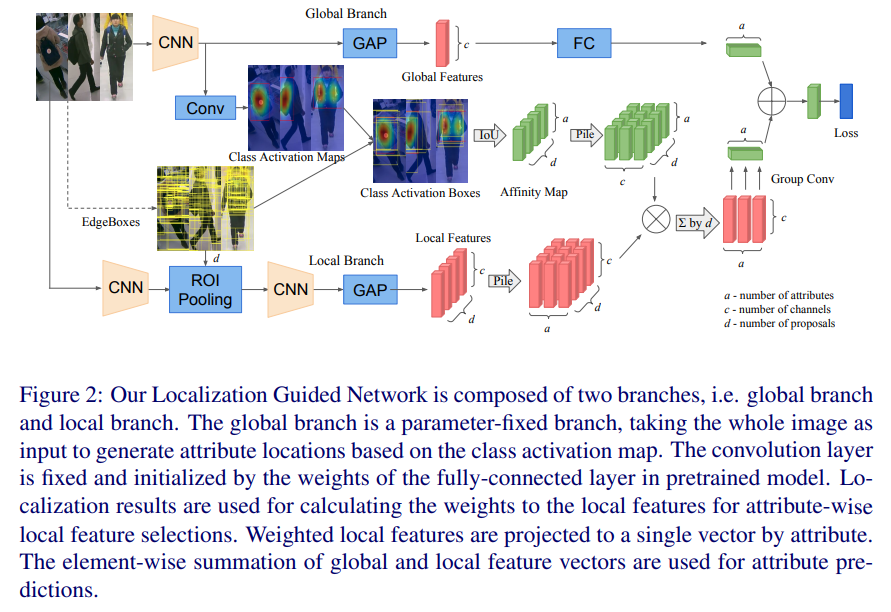
- 1.上面的是全局分支,得到属性
- 2.1 特征层卷积得到激活图,联合Edge Boxes结果对结果进行多尺度多比例扩展,得到分类层特征 2.2 卷积 + Edge Boxes结果 进行roipooling得到基于边缘框的特征 2.3 联合Edge Boxes特征和分类层特征得到最终属性结果
- 3 联合全局分支和Edge Boxes激活图分支,得到最终结果
- Edge Boxes
Sequential Prediction based Method
CNN-RNN
- paper Cnn-rnn: A unified framework for multi-label image classification
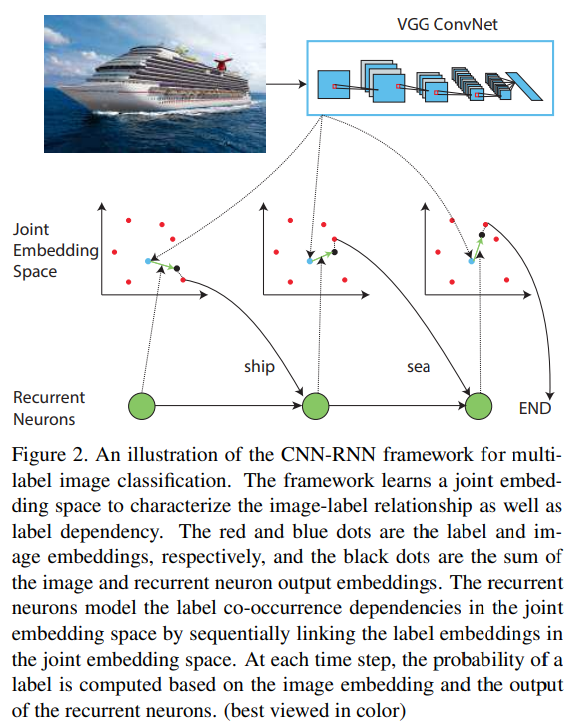
- 提出了用 联合嵌入空间对标签关联关系的学习 The framework learns a joint embedding space to characterize the image-label relationship as well as label dependency
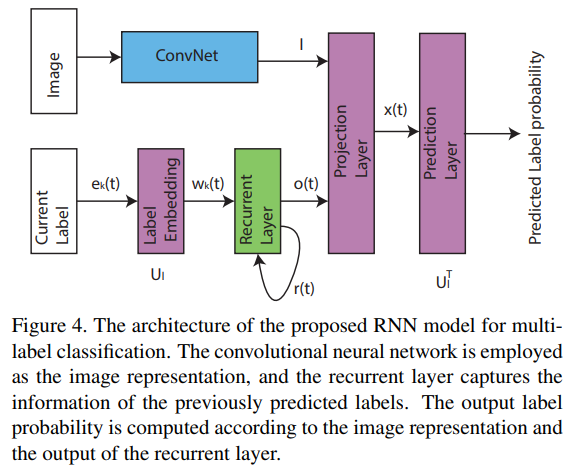
- 主要是通过标签隐向量间的关联关系加强结果,本文不是行人属性专门的文章,没有对应的结果
JRL
- paper Attribute recognition by joint recurrent learning of context and correlation
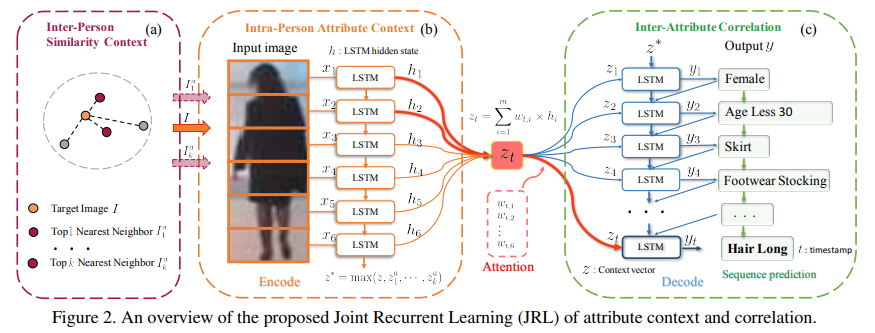
- 一方面是通过LSTM改善暴力切片分析中的上下文信息的关联性,另一方面使用了类似CNN-RNN类似想法的属性关联关系的LSTM,loss就是常规的CE
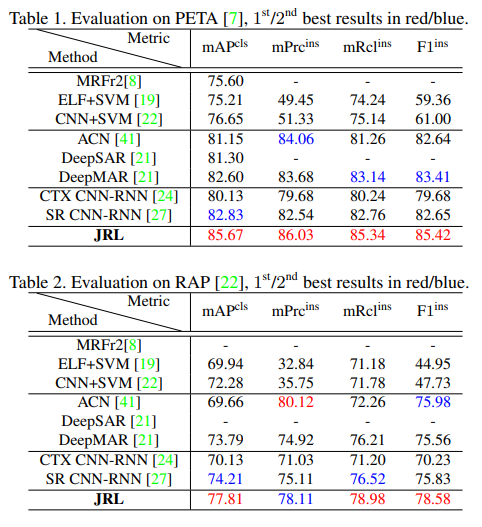
- 结果上看,相对于CNN-RNN的各种改版有较大优势
GRL
- paper Grouping attribute recognition for pedestrian with joint recurrent learning
- git https://github.com/slf12/GRLModel
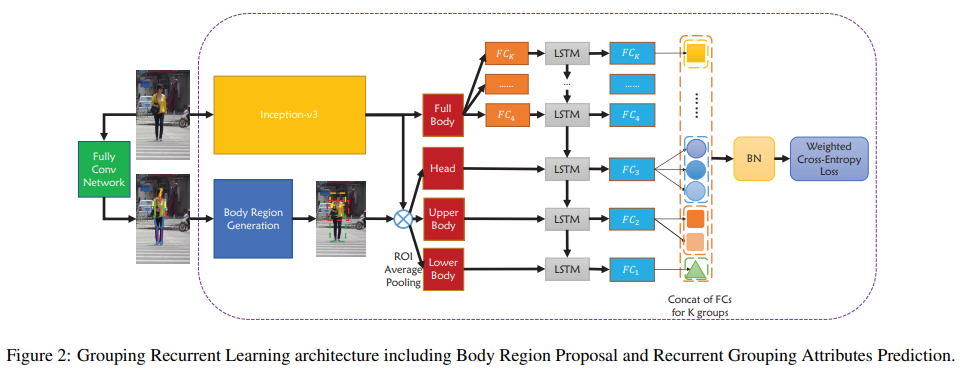
- 一个分支通过FCN生成骨骼点,然后通过区域生成层生成 头 上身 下身 三个区域,生成特征;另一个分支直接原图进入backbone得到全身特征,再对应FC出几个分支。通过LSTM对特征进行相互关联,最终得到结果
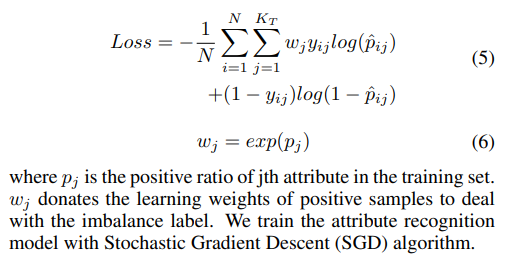
- loss上带了正项的权重用于解决标签不平衡的问题
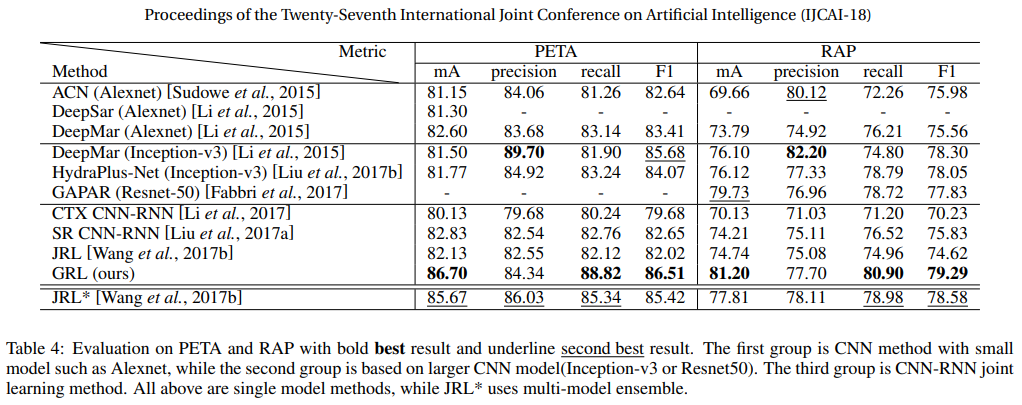
- GRL但模型干过了JRL ensemble的结果,主要优势猜测还是骨骼点带来的更精准的语义信息比起JRL的暴力分割
JCM
- paper Sequence-based person attribute recognition with joint ctc-attention model
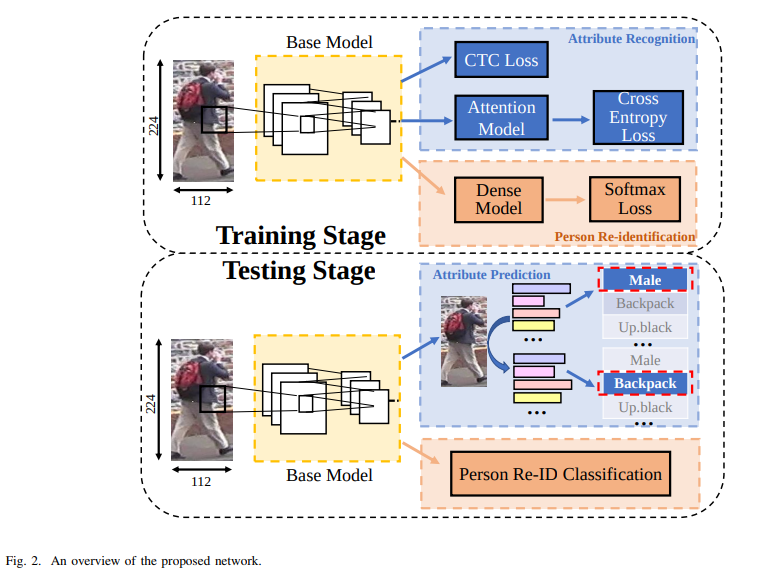
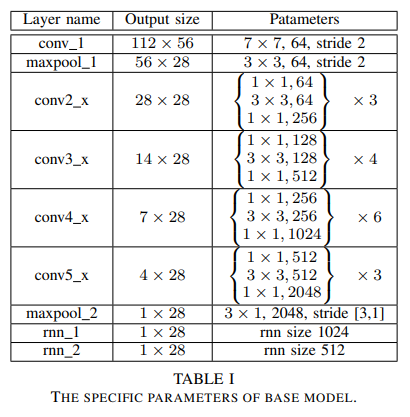
- 很简略的overview和structure,主要的contribution在于CTC loss和attention model
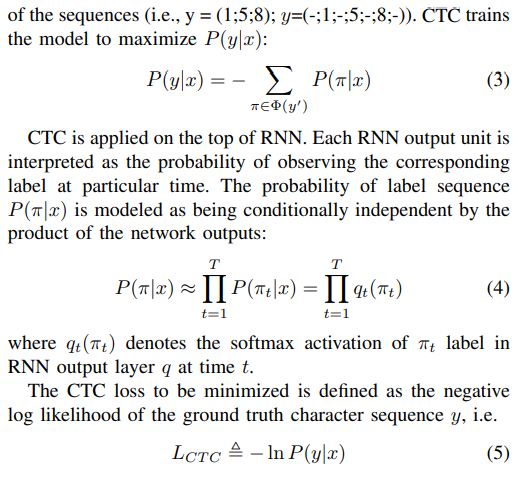
- CTC loss是联立条件概率loss,是通过关联关系提高标签准确率的思路
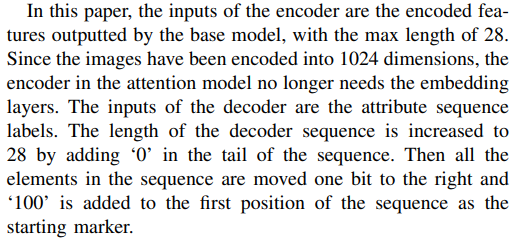
- 没有单独画图,只有这一段话说明attention model,感觉不是很清楚
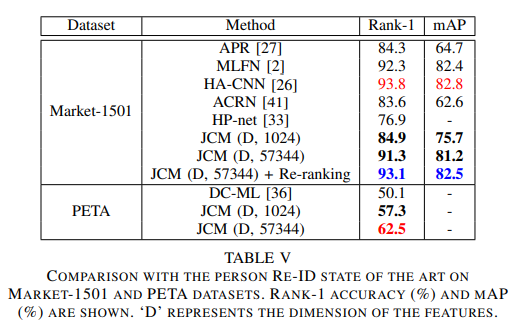
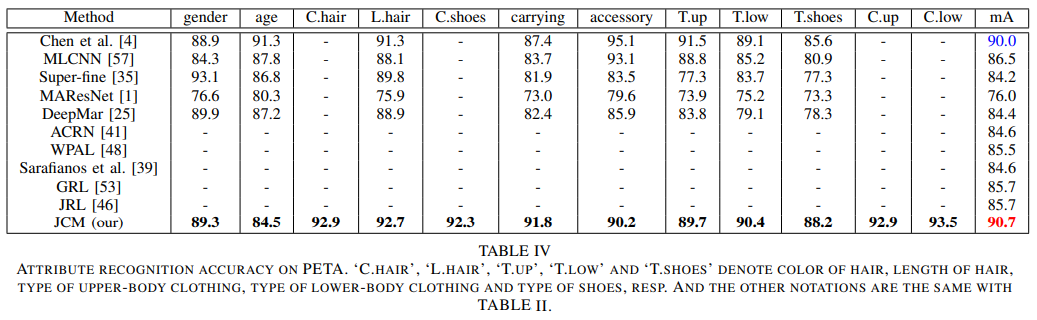
- 不仅在PETA上表现优秀,在re-id上同样有不俗的表现,同时也用实验证实了re-id任务和attention recognition任务的相辅相成
- 全文很有借鉴意义,但是attention model没有非常详细的说明,而且没有开源代码,是遗憾
RCRA
- paper Recurrent attention model for pedestrian attribute recognition
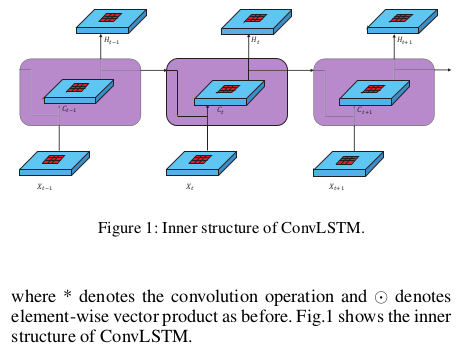

- 上来先介绍了 ConvLSTM,和LSTM的主要区别是用 Conv 取代 Linear 以保留spatial 信息
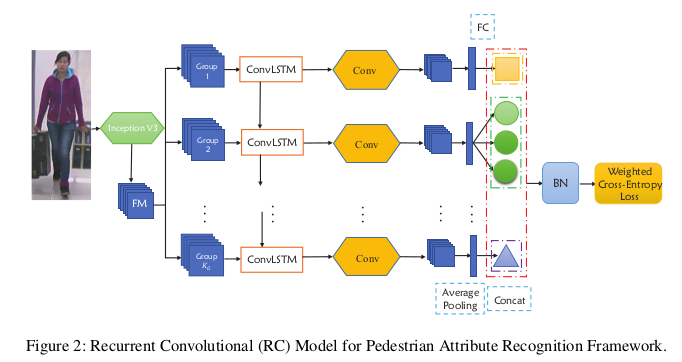
- 这是作者提出的第一个网络结果叫做 RC ,是一个常规的recurrent 结构。作者设计这个结构的初衷是从中级别卷积特征图中去挖掘标签相关性(A Recurrent Convolutional (RC) framework is proposed to mine the attribute correlations from mid-level convolutional feature maps of attribute groups.)
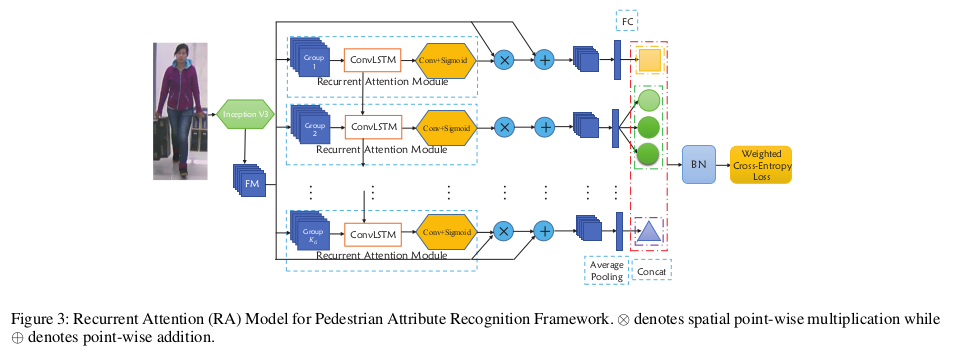
- 这是作者提出的第二个网络称之为 RA,和RC非常相似。作者设计这个结构的初衷是希望同时在组间和组内的attention机制能帮助属性识别(And a Recurrent Attention (RA) framework is formulated to recognise pedestrian attributes by group step by step in order to pay attention to both the intra-group and inter-group attention relationship.)
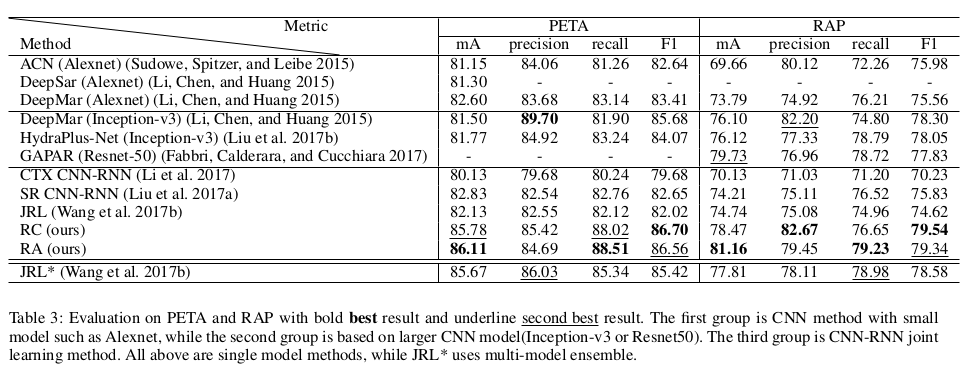
- 效果都挺不错的,在不同的指标下RC RA各有千秋
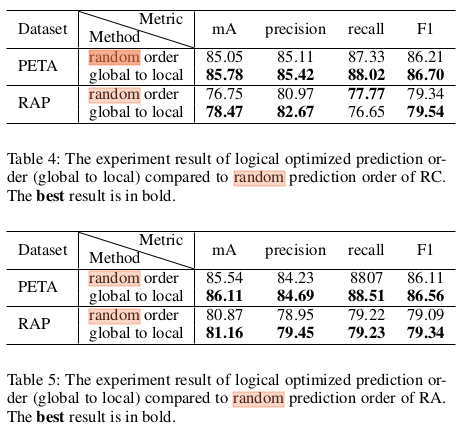
- 这个图的意思是,预测label的顺序,实验证明,从全局到局部的预测顺序比随机预测的效果要好
Dataset
overview
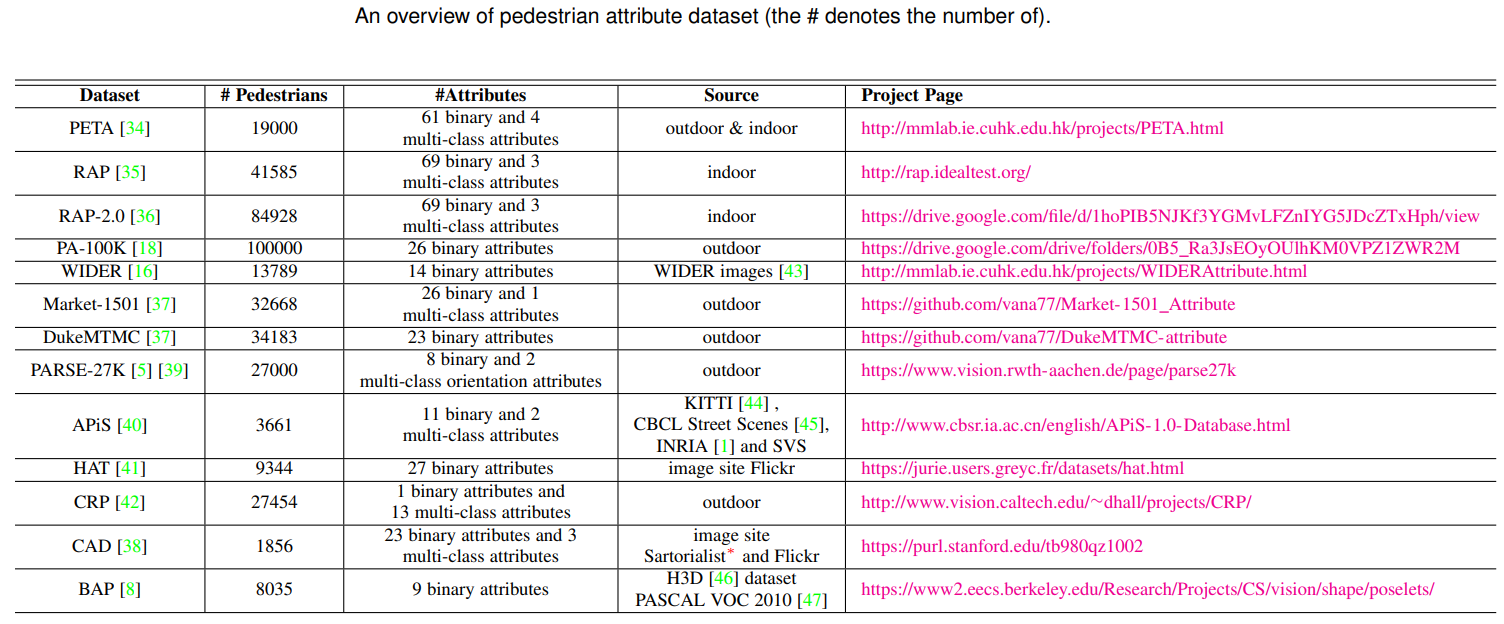
- 按学术界喜爱排序
- PETA RAP RAP2.0(19年新出,新的paper会用) PA-100K
- Market-1501 DukeMTMC (主要用于联合reid使用)
- 其他
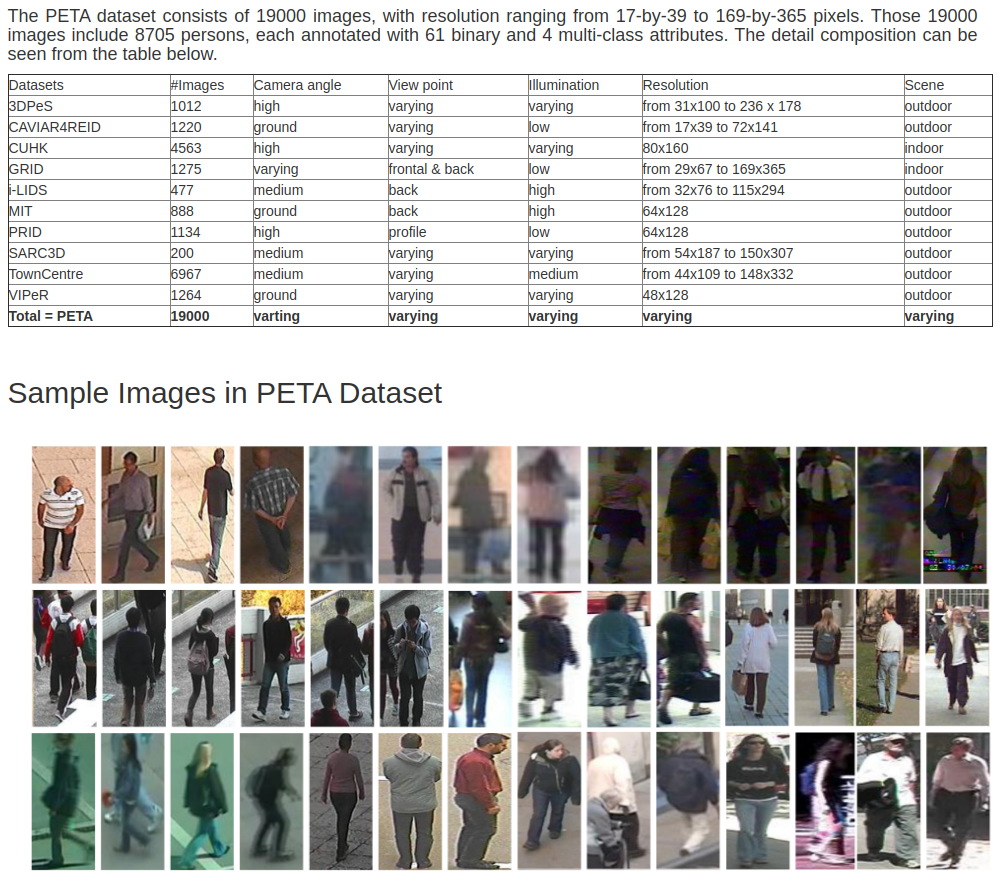
PETA
- home http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/PETA.html (港中文信息工程系14发布)
- paper http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/PETA_files/Pedestrian%20Attribute%20Recognition%20At%20Far%20Distance.pdf
- download(drop box需要翻墙) https://www.dropbox.com/s/52ylx522hwbdxz6/PETA.zip?dl=0
- The capability of recognizing pedestrian attributes, such as gender and clothing style, at far distance, is of practical interest in far-view video surveillance scenarios where face and body close-shots are hardly available. We make two contributions in this paper. First, we release a new pedestrian attribute dataset, which is by far the largest and most diverse of its kind. We show that the large-scale dataset facilitates the learning of robust attribute detectors with good generalization performance. Second, we present the benchmark performance by SVM-based method and propose an alternative approach that exploits context of neighboring pedestrian images for improved attribute inference.
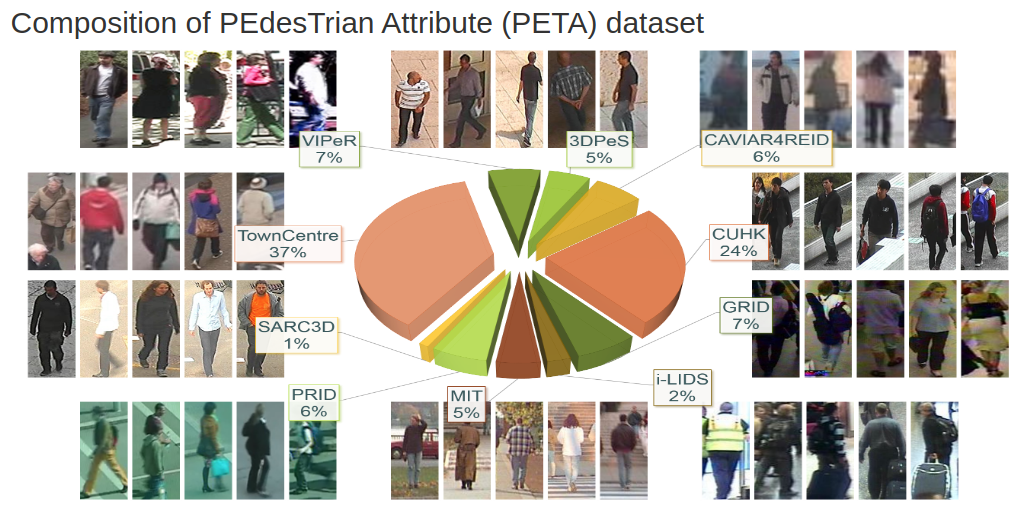
RAP Richly Annotated Pedestrian
- home(无法正常访问) http://rap.idealtest.org/
- git https://github.com/dangweili/RAP
- 1.0-paper https://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.07054.pdf
- 申请数据集的pdf RAP V1.0 Database License Agreement.pdf
- 申请数据集邮箱 jiajian2018@ia.ac.cn
- RAP has in total 41,585 pedestrian samples, each of which is annotated with 72 attributes as well as viewpoints, occlusions, body parts information.
- 2.0-paper https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8510891
- 申请数据集的pdf RAP V2.0 Database License Agreement.pdf
- 申请数据集邮箱 jiajian2018@ia.ac.cn
- RAP is a large-scale dataset which contains 84928 images with 72 types of attributes and additional tags of viewpoint, occlusion, body parts, and 2589 person identities.
PA-100K
- from sensetime
- paper https://arxiv.org/pdf/1709.09930.pdf
- git https://github.com/xh-liu/HydraPlus-Net
- download-baiduyun https://pan.baidu.com/s/1l-5a__OTwZVkhm_A16HraQ#list/path=%2F
- download-googledrive https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0B5_Ra3JsEOyOUlhKM0VPZ1ZWR2M
- we construct a new large-scale pedestrian attribute (PA) dataset named as PA-100K with 100, 000 pedestrian images from 598 scenes, and therefore offer a superiorly comprehensive dataset for pedestrian attribute recognition. To our best knowledge, it is to-date the largest dataset for pedestrian attribute recognition.
Market-1501 Attribute & DukeMTMC-attribute
- paper https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.07220.pdf
- We have manually labeled a set of pedestrian attributes for the Market-1501 dataset and the DukeMTMC-reID dataset.
- download Market-1501 https://drive.google.com/file/d/1kbDAPetylhb350LX3EINoEtFsXeXB0uW/view
- download-annotation-git https://github.com/vana77/Market-1501_Attribute (The annotations are contained in the file market_attribute.mat. “gallery_market.mat” is one prediction example. Then download the code “evaluate_market_attribute.m” in this repository, change the image path and run it to evaluate.)
| attribute | representation in file | label |
|---|---|---|
| gender | gender | male(1), female(2) |
| hair length | hair | short hair(1), long hair(2) |
| sleeve length | up | long sleeve(1), short sleeve(2) |
| length of lower-body clothing | down | long lower body clothing(1), short(2) |
| type of lower-body clothing | clothes | dress(1), pants(2) |
| wearing hat | hat | no(1), yes(2) |
| carrying backpack | backpack | no(1), yes(2) |
| carrying bag | bag | no(1), yes(2) |
| carrying handbag | handbag | no(1), yes(2) |
| age | age | young(1), teenager(2), adult(3), old(4) |
| 8 color of upper-body clothing | upblack, upwhite, upred, uppurple, upyellow, upgray, upblue, upgreen | no(1), yes(2) |
| 9 color of lower-body clothing | downblack, downwhite, downpink, downpurple, downyellow, downgray, downblue, downgreen,downbrown | no(1), yes(2) |
- download DukeMTMC baiduyun https://pan.baidu.com/s/1jS0XM7Var5nQGcbf9xUztw (密码 bhbh)
- download DukeMTMC Google Drive https://drive.google.com/open?id=1jjE85dRCMOgRtvJ5RQV9-Afs-2_5dY3O
- download-annotation-git https://github.com/vana77/DukeMTMC-attribute (The annotations are contained in the file duke_attribute.mat.)
| attribute | representation in file | label |
|---|---|---|
| gender | gender | male(1), female(2) |
| length of upper-body clothing | top | short upper body clothing(1), long(2) |
| wearing boots | boots | no(1), yes(2) |
| wearing hat | hat | no(1), yes(2) |
| carrying backpack | backpack | no(1), yes(2) |
| carrying bag | bag | no(1), yes(2) |
| carrying handbag | handbag | no(1), yes(2) |
| color of shoes | shoes | dark(1), light(2) |
| 8 color of upper-body clothing | upblack, upwhite, upred, uppurple, upgray, upblue, upgreen, upbrown | no(1), yes(2) |
| 7 color of lower-body clothing | downblack, downwhite, downred, downgray, downblue, downgreen, downbrown | no(1), yes(2) |
WIDER
- home http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/WIDERAttribute.html
- paper http://personal.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/~ccloy/files/eccv_2016_human.pdf
- download-images https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B-PXtfvNMLanWEVCaHZnR0RHSlE/view
- download-annotation http://mmlab.ie.cuhk.edu.hk/projects/WIDERAttribute_files/wider_attribute_annotation.zip
- WIDER Attribute is a large-scale human attribute dataset. It contains 13789 images belonging to 30 scene categories, and 57524 human bounding boxes each annotated with 14 binary attributes.